The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Seven Jets from Comet Hale-Bopp Credit:
13/11/1996
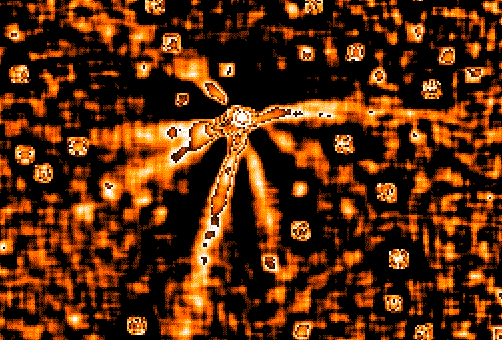
Comet Hale-Bopp is turning out to be quite unusual. One reason is the great amount of jet activity at such a large distance from the Sun. In the above false-color image, no less than seven jets can be seen emanating from Hale-Bopp's coma. As a comet nears the Sun, it's surface warms causing jets of previously trapped gas and dust to stream away from the nucleus. Astronomers continue to study Comet Hale-Bopp's unusual jet activity and wonder how much about the early Solar System Hale-Bopp will teach them, and how bright Hale-Bopp will ultimately become.