The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Prominent Solar Prominence
27/01/1997
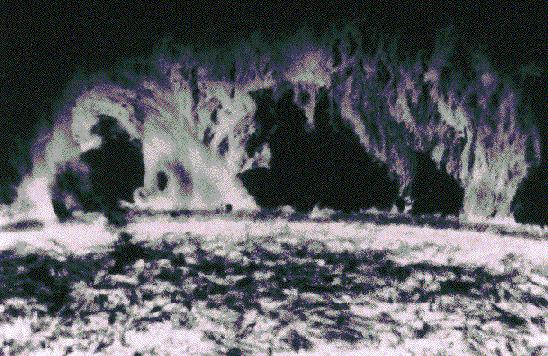
One of the most spectacular solar sights is a prominence. A solar prominence is a cloud of solar gas held above the Sun's surface by the Sun's magnetic field. The Earth would easily fit under one of the loops of the prominence shown in the above picture. A quiescent prominence typically lasts about a month, and may erupt in a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) expelling hot gas into the Solar System. Although thought by many to be related to the magnetic field, the energy mechanism behind a Solar prominence is still unknown.