The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
The Sun Changes
13/04/1998
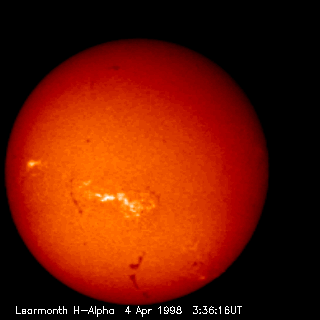
Our Sun changes every day. This recent picture was taken in a very specific red color called Hydrogen-Alpha. Dark spots that might appear on the image are usually sunspots, dark magnetic depressions that are slightly cooler than the rest of the Sun's surface. Bright spots that might appear are usually plages, active regions that are slightly hotter than the rest of the Sun's surface. Over the next few years the average number of sunspots and plages will increase until "Solar Maximum" occurs in 2001. The Sun usually goes through a maximum and minimum every 11 years. From 1645 to 1715, however, almost no sunspots at all were recorded, for reasons unknown. (An updated picture can be found here.)