The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Solar Flares Cause Sun Quakes
01/06/1998
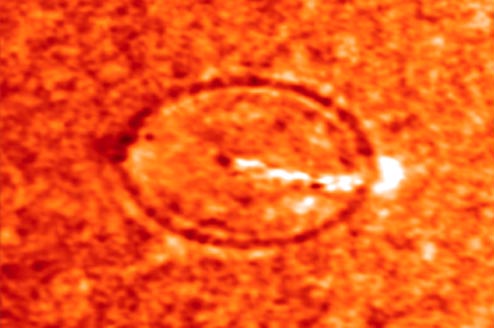
An 11th magnitude quake has been recorded on the Sun, immediately following a moderate solar flare. The quake was the first ever recorded on the Sun, but only because astronomers have only recently figured out when and how to find them using the orbiting SOHO spacecraft. Dark waves from the quake can be seen in the above picture spreading out from an explosive bright flare. The solar ripples are similar in appearance to waves caused by a rock thrown into a pond. The magnitude and evolution of these quakes gives information about the physical nature of solar flares, the surface of the Sun, and even the Sun's interior.