The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Southern Neptune
27/06/1998
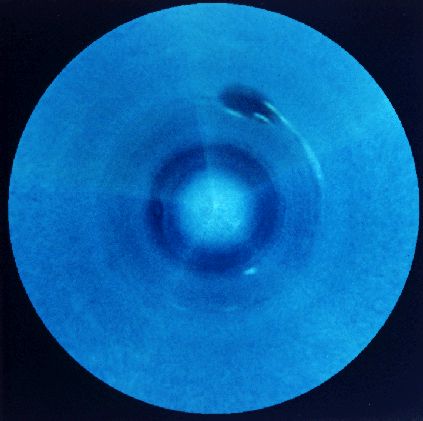
Neptune, the Solar System's outermost gas giant planet, is 30 times farther from the Sun than Earth. Twelve years after a 1977 launch, Voyager 2 flew by Neptune and found surprising activity on a planet that receives only 3 percent as much sunlight as Jupiter. In its brief but tantalizing close-up glimpse of this dim and distant world, the robot spacecraft recorded pulses of radio emission, zonal cloud bands, and large scale storm systems with up to 1500 mile per hour winds - the strongest measured on any planet. This mosaic of 5 Voyager images shows Neptune's Southern Hemisphere. Cloud bands and the Earth-sized, late "Great Dark Spot" with trailing white clouds located at about 22 degrees southern latitude are clearly visible. The distance from the Great Dark Spot feature to Neptune's South Pole (image center) is about 17,000 miles.