The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
SOHO Composite: Coronal Mass Ejection
20/08/1998
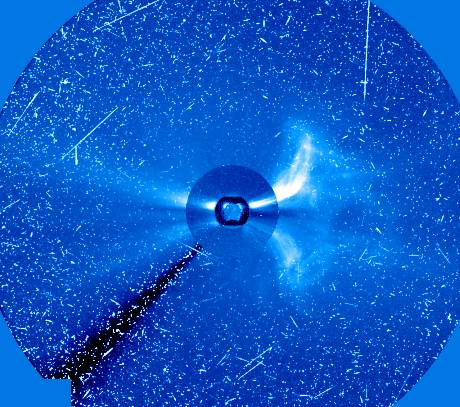
This complex composite image of an ominous and spectacular event - an expanding storm of energetic particles from the Sun - was constructed using data recorded by the SOHO spacecraft on November 6, 1997. Four images from two SOHO (Solar Orbiting Heliospheric Observatory) instruments have been nested to show the ultraviolet Sun at center and a large eruption of material from the right-hand solar limb. Known as a Coronal Mass Ejection or CME, the expanding cloud has become relatively cool and dark in the middle with bright edges still connected to the solar surface. High energy protons have peppered the SOHO detectors causing the crazed streaks and blemishes. The picture covers a region extending about 13.5 million miles from the Sun (32 Solar Radii). On June 25, after successfully completing its planned mission, contact with SOHO was lost -- but has recently been re-established! Hopefully SOHO will soon be able to continue operating in an extended mission phase.