The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Autumn and the Active Sun
23/09/1998
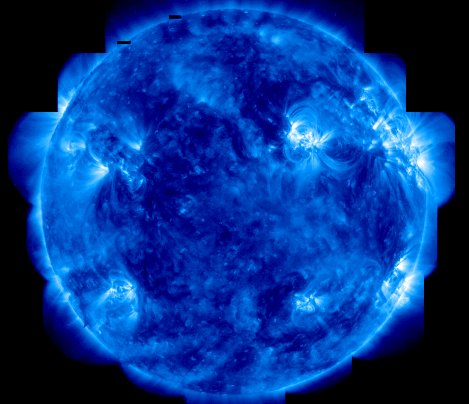
As the Sun heads South, crossing the celestial equator today at 1:37 a.m. Eastern Time, Autumn begins for Earth's Northern Hemisphere. This Autumnal Equinox finds an increasingly active Sun steadily approaching a solar cycle maximum expected around the year 2003. The solar activity cycle is driven by a periodic winding up of the Sun's internal magnetic field. This colorized picture is a mosaic of recent ultraviolet images from the orbiting TRACE satellite sensitive to light emitted by highly charged iron atoms. Growing in number, the intricate structures visible are the Sun's hot active regions with temperatures over a million degrees Fahrenheit and their associated magnetic loops.