The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Sunspot Up Close
05/10/1998
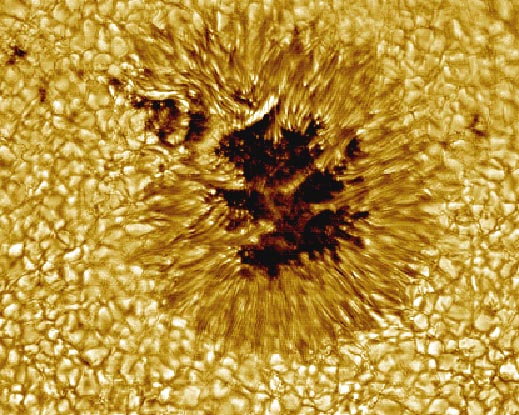
Sometimes, small regions of the Sun appear unusually dark. Visible above is a close-up picture of a sunspot, a depression on the Sun's face that is slightly cooler and less luminous than the rest of the Sun. The Sun's complex magnetic field creates this cool region by inhibiting hot material from entering the spot. Sunspots can be larger than the Earth and typically last for only a few days. This high-resolution picture also shows clearly that the Sun's face is a bubbling sea of separate cells of hot gas. These cells are known as granules. A solar granule is about 1000 kilometers across and lasts about 10 minutes. After that, many granules end up exploding.