The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
The Nearest Stars
21/04/1999
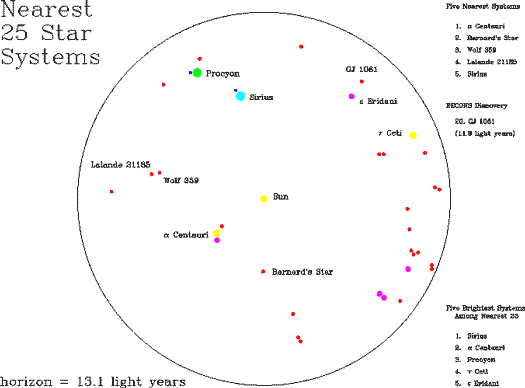
Which stars are closest to the Sun? The closest is Proxima Centauri, one of three stars that orbit each other about 4 light-years away in the Alpha-Centauri system. Alpha Centauri is easily visible from Earth's Southern Hemisphere. Next is Barnard's Star, a dim star visible with a telescope in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, is part of the fifth closest star system, from which light takes 8.6 years to reach us. The nearest 25 star systems are shown on the above map, out to 13 light-years. Past that there are probably stars so dim that their proximity has not yet been discovered. Research continues in trying to identify an estimated 130 missing star systems out to 32 light-years.