The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Total Eclipse for Europe
10/08/1999
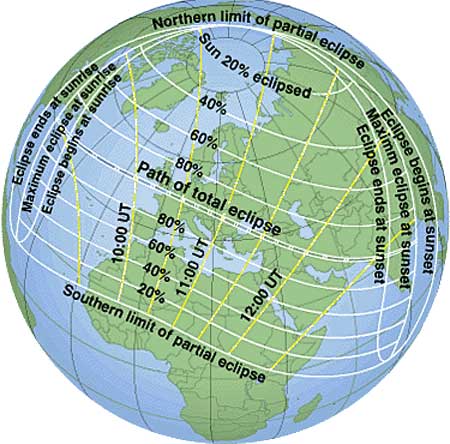
The last total solar eclipse of this millennium will be visible for a few minutes tomorrow from a narrow path in Europe and Asia. There, millions of sightseers will witness the Moon move directly between the Earth and Sun, covering up the Sun completely. Observers not besieged by clouds may get to see the Sun's large and flowing corona first hand. A partial eclipse of the Sun, where part of the Sun is still visible, can be witnessed throughout the rest of Europe and much of Northern Africa and Asia. Precise locations of total and partial eclipse are shown on the above map. In modern times, eclipses are precisely predicted and well understood. In fact, anyone can see this total solar eclipse live on the web. In ancient times, though, eclipses frequently startled large populations, who interpreted them in ways that changed the course of wars and empires.