The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Brown Sun Bubbling
10/01/2000
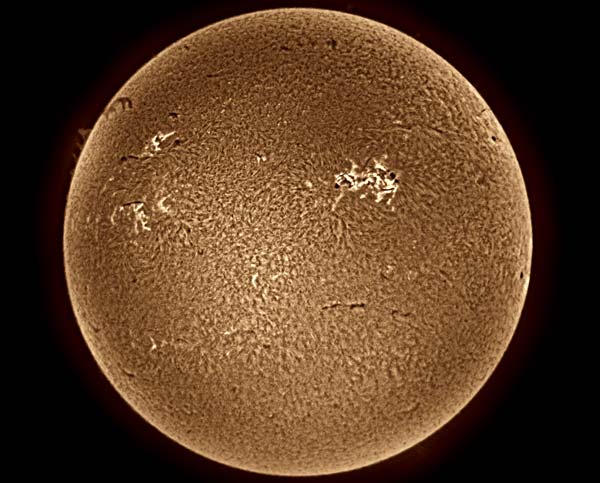
Our Sun may look like all soft and fluffy, but its not. Our Sun is an extremely large ball of bubbling hot gas, mostly hydrogen gas. The above picture was taken in a specific color of light emitted by hydrogen gas called Hydrogen-alpha. Granules cover the solar photosphere surface like shag carpet, interrupted by bright regions containing dark sunspots. Visible at the left edge is a solar prominence. Our Sun glows because it is hot, but it is not on fire. Fire is the rapid acquisition of oxygen, and there is very little oxygen on the Sun. The energy source of our Sun is the nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium deep within its core. Astronomers are still working to understand, however, why so few neutrinos are measured from the Sun's core.