The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
X-Rays From Sirius B
06/10/2000
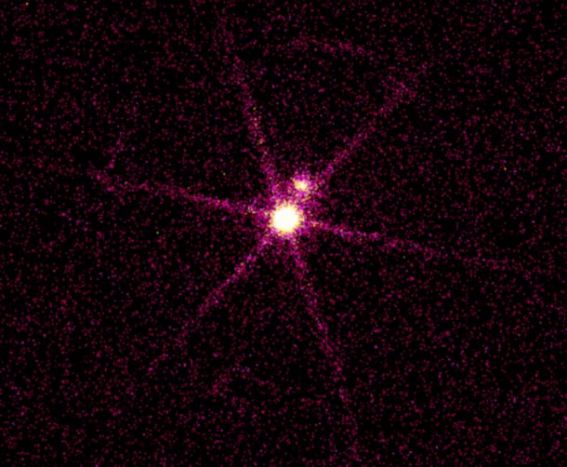
In visible light Sirius A (Alpha Canis Majoris) is the brightest star in the night sky, a closely watched celestial beacon throughout recorded history. Part of a binary star system only 8 light-years away, it was known in modern times to have a small companion star, Sirius B. Sirius B is much dimmer and appears so close to the brilliant Sirius A that it was not actually sighted until 1862, during Alvan Clark's testing of a large, well made optical refracting telescope. For orbiting x-ray telescopes, the Sirius situation is exactly reversed, though. A smaller but hotter Sirius B appears as the overwhelmingly intense x-ray source in this Chandra Observatory x-ray image (lines radiating from Sirius B are image artifacts). The fainter source seen at the position of Sirius A may be largely due to ultraviolet light from the star leaking into the x-ray detector. With a surface temperature of 25,000 kelvins, the mass of the Sun, and a radius just less than Earth's, Sirius B is the closest known white dwarf star. Can you guess what makes Sirius B like Neptune, the Sun's most distant gas giant planet? While still unseen, the presence of both celestial bodies was detected based on their gravitational influence alone ... making them early examples of dark matter.