The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Jupiter Swallows Comet Shoemaker Levy 9
05/11/2000
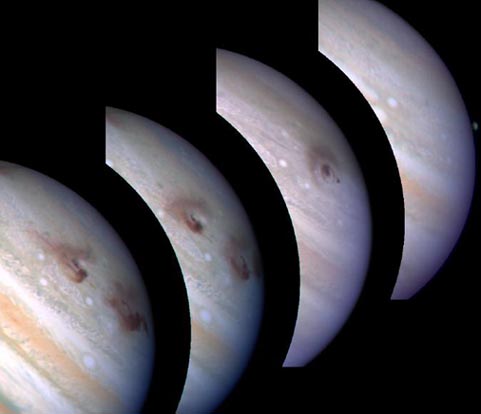
What happens when a comet encounters a planet? If the planet has a rocky surface, a huge impact feature will form. A giant planet like Jupiter, however, is mostly gas. When Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 struck Jupiter in 1994, each piece was swallowed into the vast Jovian atmosphere. Pictured above is a time-lapse sequence of the result of two fragments striking Jupiter. As the comet plunged in, it created large dark marks that gradually faded. The high temperature of gas under Jupiter's cloud tops surely caused the comet fragment to melt before it plunged very far. Because Jupiter is much more massive than any comet, the orbit of Jupiter around the Sun did not change noticeably.