The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Close-Up of Aurora on Jupiter
19/12/2000
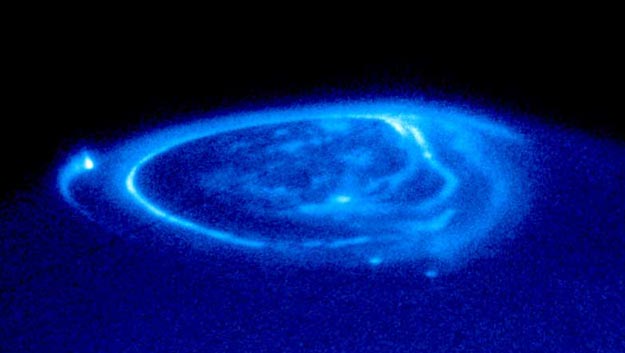
Jupiter has aurorae. Like Earth, the magnetic field of the gas giant funnels charged particles released from the Sun onto the poles. As these particles strike the atmosphere, electrons are temporarily knocked away from existing gas molecules. Electric force attracts these electrons back. As the electrons recombine to remake neutral molecules, auroral light is emitted. In the above recently released photograph by the Hubble Space Telescope taken in ultraviolet light, the aurorae appear as annular sheets around the pole. Unlike Earth's aurorae, Jupiter's aurorae include several bright streaks and dots. These marks are caused by magnetic flux tubes connecting Jupiter to its largest moons. Specifically, Io caused the bright streak on the far left, Ganymede caused the bright dot below center, and Europa caused the dot to its right.