The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Under A Sunspot
08/11/2001
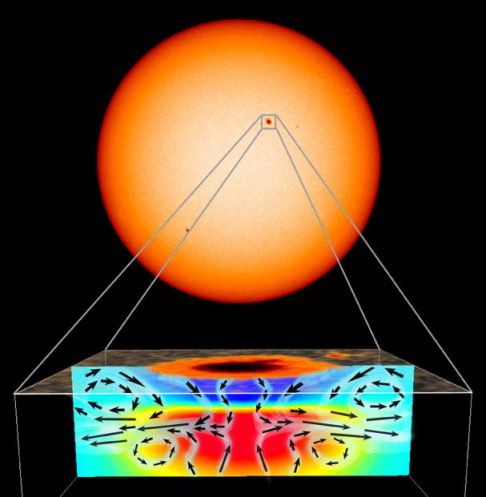
At the Sun's surface, sunspots are known to be dark, planet-sized regions of intense magnetic fields. But what lies below? Using observations from the Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) instrument aboard the space-based SOHO observatory, astronomers have derived this premier picture of the flow of material just beneath a visible sunspot. The MDI data indicate that immediately under the sunspot a strong inflowing current exists, shown above by the dark arrows. This converging undertow pulls near-surface material toward the spot and prevents the concentrated magnetic fields from flying apart, like repelling poles of iron magnets. Such a configuration appears to divert the normal flow of plasma bubbling up from the solar interior, creating a self-sustaining sunspot. The MDI instrument can explore the properties of the solar interior by detecting motions produced by sound waves as they interact at the solar surface.