The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Stereo Eros
01/03/2003
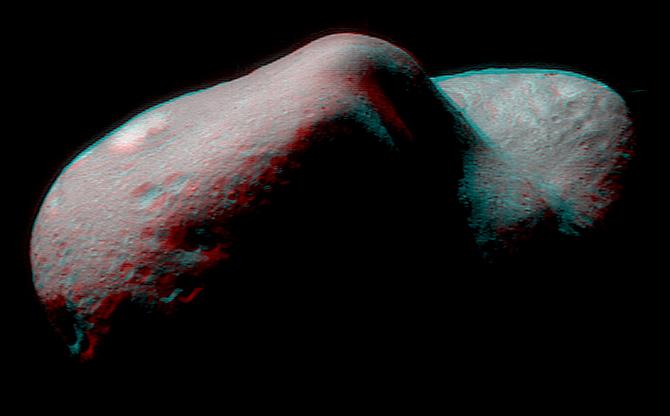
Get out your red/blue glasses and float next to asteroid 433 Eros, 170 million kilometers away! Orbiting the Sun once every 1.8 earth-years, asteroid Eros is a diminutive 40 x 14 x 14 kilometer world of undulating horizons, craters, boulders and valleys. Its unsettling scale and bizarre shape are emphasized in this picture - a mosaic of images from the NEAR Shoemaker spacecraft processed to yield a stereo anaglyphic view. Along with dramatic chiaroscuro, NEAR's 3-D imaging provided important measurements of the asteroid's landforms and structures, and clues to the origin of this city-sized chunk of solar system. The smallest features visible here are about 30 meters across. After spending a year in orbit around Eros, the historic Near Shoemaker spacecraft made the first ever landing on an asteroid's surface February 12, 2001.