The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Orange Sun Simmering
29/07/2003
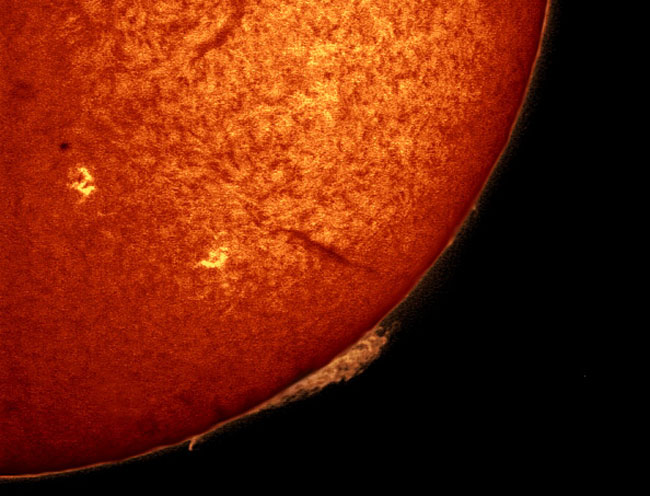
ven a quiet Sun is a busy place. The above image, taken in a single color of light called Hydrogen Alpha, records a great amount of detail of the simmering surface of our parent star. The gradual darkening towards the Sun's edge, called limb darkening, is caused by increased absorption of relatively cool solar gas. Further over the edge, a giant prominence is visible, while a different prominence can be seen in silhouette as the dark streak near the image center. Two active areas of the Sun are marked by bright plages. The above amateur photograph of the Sun was taken just last month through a small telescope and a standard digital camera. In contrast, there are times when our Sun appears much more active.