The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Powerful Solar Flare
29/10/2003
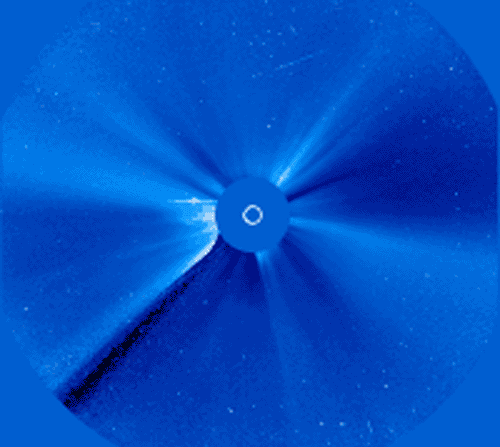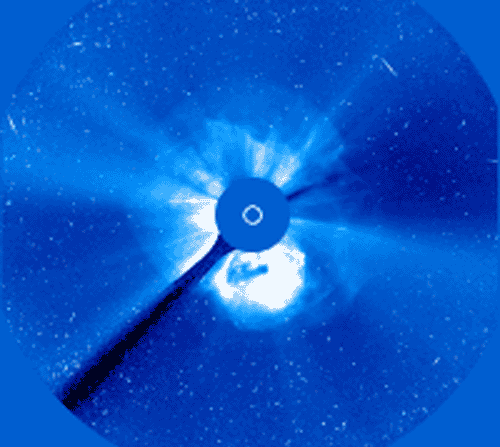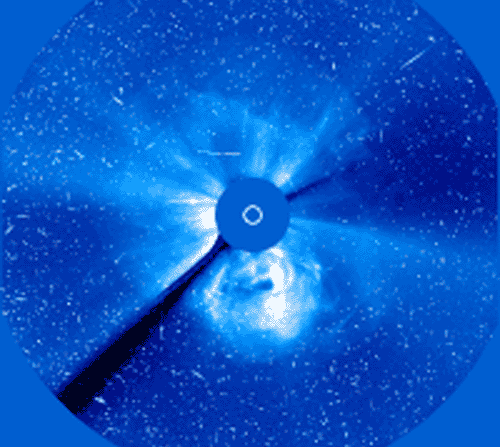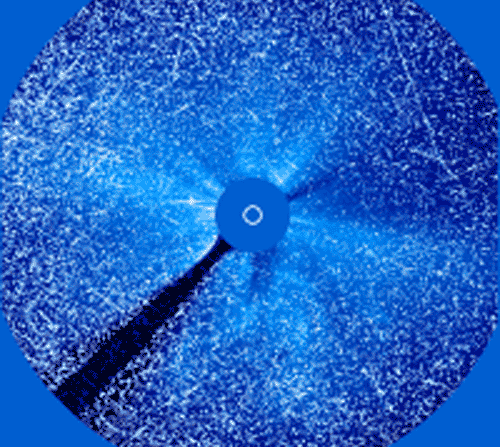
Yesterday, our Sun produced one of the most powerful solar flares in recorded history. Seen across the electromagnetic spectrum, the Sun briefly became over 100 times brighter in X-rays than normal. Over the next few days, as energetic particles emitted from these regions strike the Earth, satellite communications might be affected and auroras might develop. The flare and resulting CME, emitted from giant sunspot group 10486, was captured above as it happened by the by the LASCO instrument aboard the Sun-orbiting SOHO satellite. The disk of the Sun is covered to accentuate surrounding areas. The time-lapse movie shows the tremendous explosion in frames separated in real time by about 30 minutes each. The frames appear progressively noisier as protons from the flare begin to strike the detector. The SOHO satellite has been put in a temporary safe mode to avoid damage from the solar particle storm.