The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
A Late Leonid from a Sparse Shower
25/11/2003
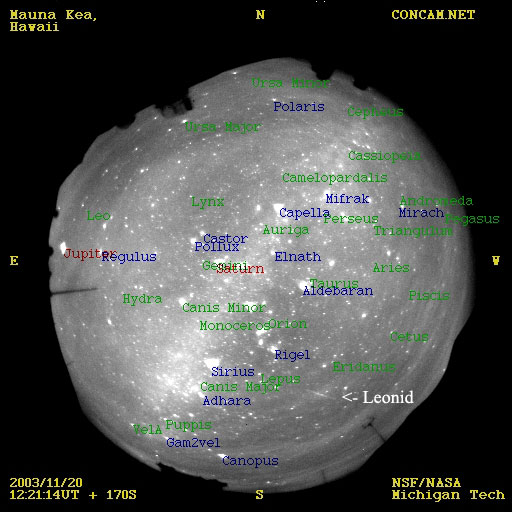
The 2003 Leonids Meteor Shower contained relatively few meteors. As expected and unlike the last few years, the Earth just did not pass through any dense particle streams left over by the Sun-orbiting Comet Tempel-Tuttle. Preliminary reports had the peak meteor rates only as high as about one relatively faint meteor a minute even from good locations at good times. Pictured above is one of the brighter Leonids of 2003, caught by one of the continuously operating night sky web cameras (CONCAMs) of the global Night Sky Live project. The fisheye image shows the night sky from horizon to horizon above Mauna Kea, Hawaii, USA. The image is annotated with several bright stars and planets. Note that this meteor, as do all Leonids, appears to emanate from the constellation Leo, labeled on the upper left. Although the peak of the Leonids this year was on November 19, this meteor flashed through the sky the next night.