The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Comet Bradfield Passes the Sun
19/04/2004
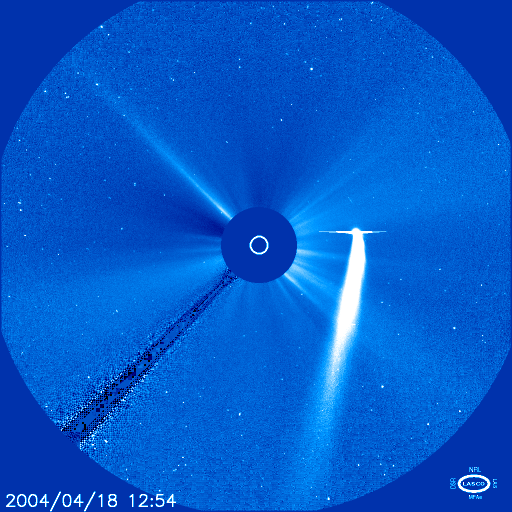
Today, Comet Bradfield is passing the Sun. The above image, taken yesterday in the direction of the Sun by the SOHO LASCO instrument, shows the comet and its dust tail as the elongated white streak. The Sun would normally be seen in the very center but has been blocked from view. Comet C/2004 F4 (Bradfield) was discovered just one month ago and has brightened dramatically as it neared the Sun. Careful sky gazers can see Comet Bradfield with the unaided eye near the Sun, although NASA's sun-orbiting SOHO satellite has the best view. During the day, Comet Bradfield will continually shift inside the LASCO frame as it rounds the Sun. There is even the possibility that the comet will break up. If not, the bright comet's trajectory will carry it outside the field of LASCO sometime tomorrow. Along with T7 and Q4, Comet Bradfield is now the third comet that is currently visible on the sky with the unaided eye, the most ever of which we are aware and quite possibly the most in recorded history.