The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Cassiopeia A in a Million
26/08/2004
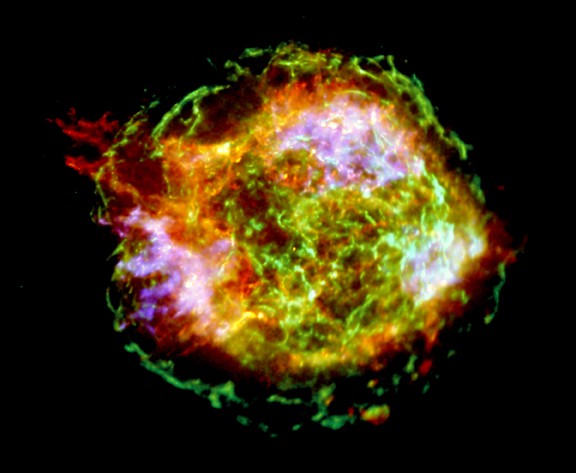
One million seconds of x-ray image data were used to construct this view of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A, the expanding debris cloud from a stellar explosion. The stunningly detailed image from the Chandra Observatory will allow an unprecedented exploration of the catastrophic fate that awaits stars much more massive than the Sun. Seen in false-color, Cas A's outer green ring, 10 light-years or so in diameter, marks the location of the expanding shock from the original supernova explosion. At about 10 o'clock around the ring, a structure extends beyond it, evidence that the initial explosion may have also produced energetic jets. Still glowing in x-rays, the tiny point source near the center of Cas A is a neutron star, the collapsed remains of the stellar core. While Cas A is about 10,000 light-years away, light from the supernova explosion first reached Earth just over 300 years ago.