The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Sunset Analemma
21/06/2019
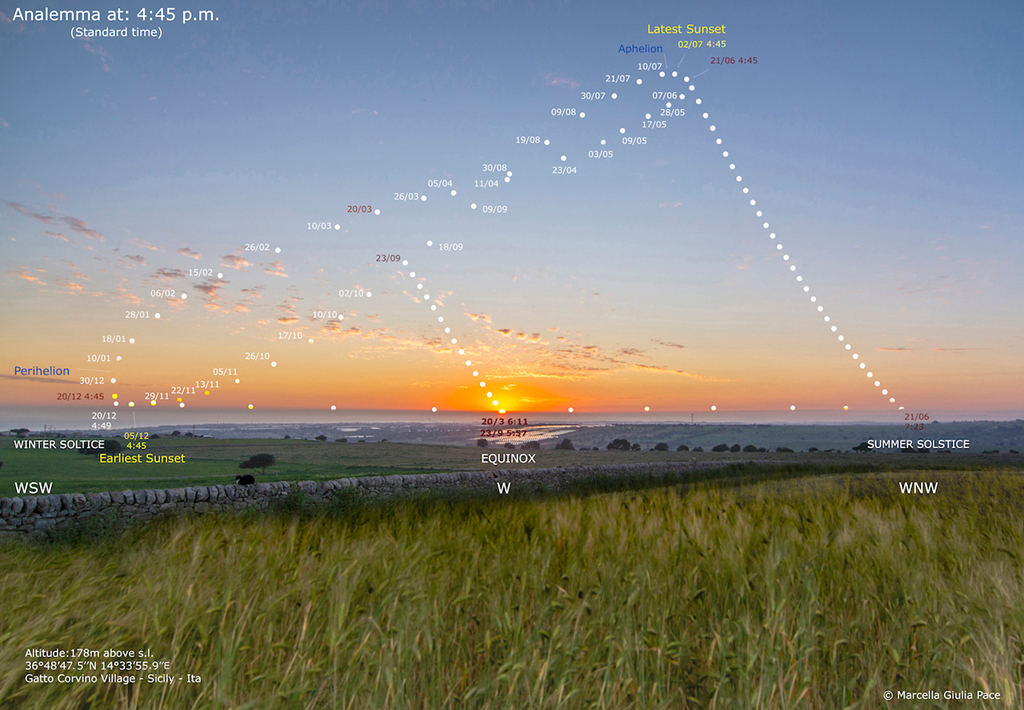
Today, the solstice is at 15:54 Universal Time, the Sun reaching the northernmost declination in its yearly journey through planet Earth's sky. A June solstice marks the astronomical beginning of summer in the northern hemisphere and winter in the south. It also brings the north's longest day, the longest period between sunrise and sunset. In fact the June solstice sun is near the top, at the most northern point in the analemma or figure 8 curve traced by the position of the Sun in this composite photo. The analemma was created (video) from images taken every 10 days at the same time from June 21, 2018 and June 7, 2019. The time was chosen to be the year's earliest sunset near the December solstice, so the analemma's lowest point just kisses the unobstructed sea horizon at the left. Sunsets arranged along the horizon toward the right (north) are centered on the sunset at the September equinox and end with sunset at the June solstice.