The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Moon Mountains Magnified during Ring of Fire Eclipse
22/06/2020
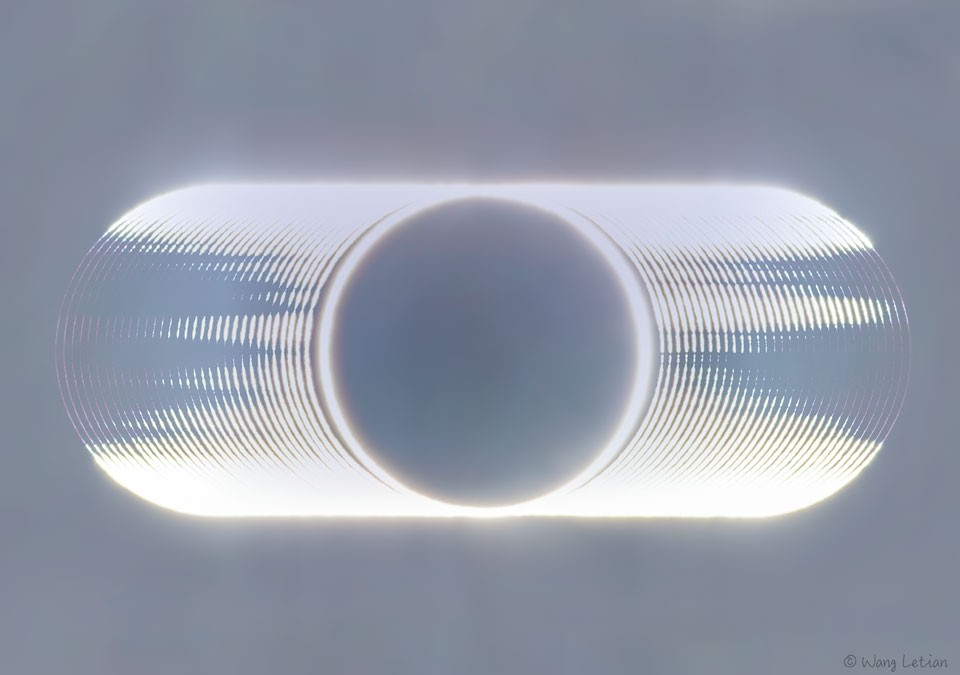
What are those dark streaks in this composite image of yesterday's solar eclipse? They are reversed shadows of mountains at the edge of the Moon. The center image, captured from Xiamen, China, has the Moon's center directly in front of the Sun's center. The Moon, though, was too far from the Earth to completely block the entire Sun. Light that streamed around all of the edges of the Moon is called a ring of fire. Images at each end of the sequence show sunlight that streamed through lunar valleys. As the Moon moved further in front of the Sun, left to right, only the higher peaks on the Moon's perimeter could block sunlight. Therefore, the dark streaks are projected, distorted, reversed, and magnified shadows of mountains at the Moon's edge. Bright areas are called Baily's Beads. Only a narrow swath across Earth's Eastern Hemisphere was able to see yesterday's full annular solar eclipse. Next June, though, a narrow swath across Earth's Northern Hemisphere will be able to see the next annular solar eclipse. A total solar eclipse will be visible at the bottom of the world near the end of this year. Gallery: Notable images of the Annular Solar Eclipse of 2020 June submitted to APOD