The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Biomarker Phosphine Discovered in the Atmosphere of Venus
15/09/2020
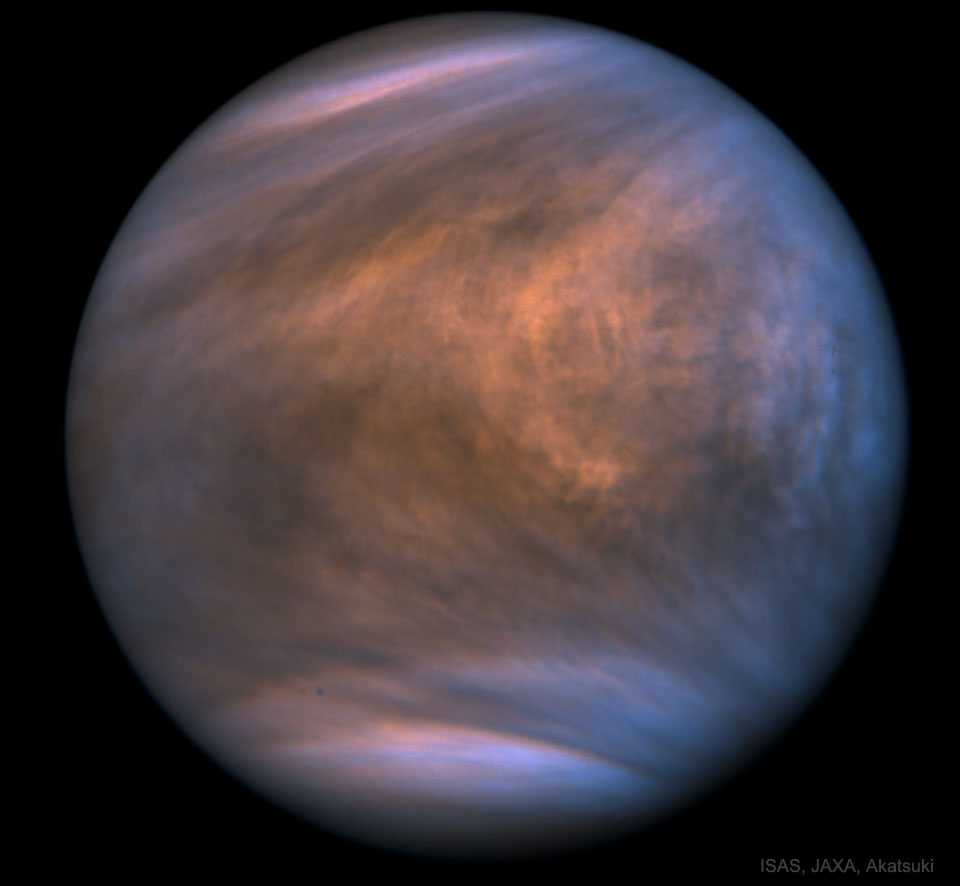
Could there be life floating in the atmosphere of Venus? Although Earth's planetary neighbor has a surface considered too extreme for any known lifeform, Venus' upper atmosphere may be sufficiently mild for tiny airborne microbes. This usually disfavored prospect took an unexpected upturn yesterday with the announcement of the discovery of Venusian phosphine. The chemical phosphine (PH3) is a considered a biomarker because it seems so hard to create from routine chemical processes thought to occur on or around a rocky world such as Venus -- but it is known to be created by microbial life on Earth. The featured image of Venus and its thick clouds was taken in two bands of ultraviolet light by the Venus-orbing Akatsuki, a Japanese robotic satellite that has been orbiting the cloud-shrouded world since 2015. The phosphine finding, if confirmed, may set off renewed interest in searching for other indications of life floating high in the atmosphere of our Solar System's second planet out from the Sun. Experts Debate: How will humanity first discover extraterrestrial life?