The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
Saturn and Jupiter in Summer 2020
12/12/2020
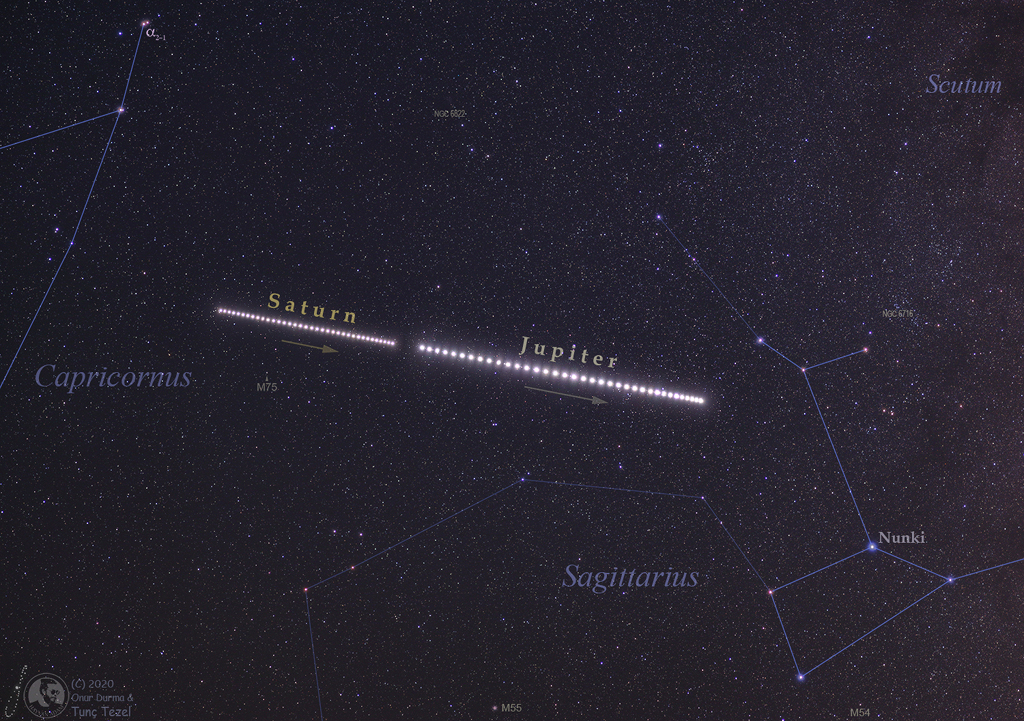
During this northern summer Saturn and Jupiter were both near opposition, opposite the Sun in planet Earth's sky. Their paired retrograde motion, seen about every 20 years, is followed from 19 June through 28 August in this panoramic composite as they wander together between the stars in western Capricornus and eastern Sagittarius. But this December's skies find them drawing even closer together. Jupiter and Saturn are now close, bright celestial beacons in the west after sunset. On solstice day December 21 they will reach their magnificent 20 year Great Conjunction. Then the two largest worlds in the Solar System will appear in Earth's sky separated by only about 1/5 the apparent diameter of a Full Moon.