Ultraviolet Light
Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. Ultraviolet observations are crucial for studying hot astronomical objects like accretion disks around black holes.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Ultraviolet Light"
A Complete Aurora Credit:
02/04/1997
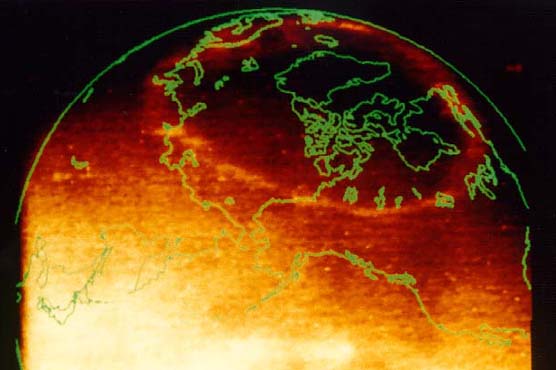
Aurora frequently make complete rings around a pole of the Earth. This particular "crown", visible in orange near the top of this image, was taken by the orbiting Polar spacecraft about one year ago and released by NASA last month. A complete auroral oval is normally hard to photograph because part of it usually occurs over a brightly sunlit portion of the Earth. Polar's Earth Camera, however, can be programmed to filter out all but a certain type of ultraviolet light. In this "color", atmospheric oxygen can glow brighter than reflected sunlight. People with normal eyesight living near the Great Lakes in North America would have been able to see this aurora, were it not daytime!