White Dwarf
The dense, hot core left behind after a low- or intermediate-mass star expels its outer layers. White dwarfs are composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter and no longer undergo fusion.
Source: chandra.harvard.edu
APODs including "White Dwarf"
MyCn18: An Hourglass Nebula
14/09/1997
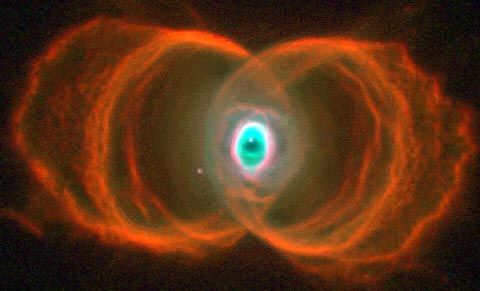
The sands of time are running out for the central star of this hourglass-shaped planetary nebula. With its nuclear fuel exhausted, this brief, spectacular, closing phase of a Sun-like star's life occurs as its outer layers are ejected - its core becoming a cooling, fading white dwarf. Astronomers have recently used the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to make a series of images of planetary nebulae, including the one above. Here, delicate rings of colorful glowing gas (nitrogen-red, hydrogen-green, and oxygen-blue) outline the tenuous walls of the "hourglass". The unprecedented sharpness of the HST images has revealed surprising details of the nebula ejection process and may help resolve the outstanding mystery of the variety of complex shapes and symmetries of planetary nebulae.