White Dwarf
The dense, hot core left behind after a low- or intermediate-mass star expels its outer layers. White dwarfs are composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter and no longer undergo fusion.
Source: chandra.harvard.edu
APODs including "White Dwarf"
Monitoring M2-9
18/06/2007
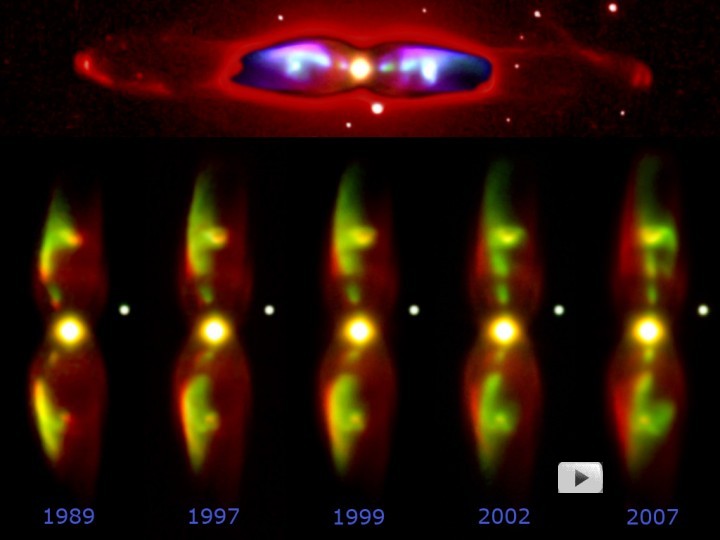
ring the myriad shapes found in the cosmic zoo of planetary nebulae, some astronomers have focused on the intriguing example of M2-9. About 2,100 light-years away and over one light-year across, M2-9 is known as a twin jet or butterfly nebula in reference to its striking bipolar symmetry. Monitoring M2-9 over many years from ground based telescopes has revealed the dramatic west to east (left to right) progression of features illustrated in this collage. The apparent motion could well be caused by an energetic rotating beam sweeping across the nebular material. Astronomers argue that the beam is collimated by interacting stellar winds in a double star system at the center of M2-9. The binary system of a giant star and hot white dwarf star orbit each other about once every 120 years. Click on the image to watch an animated gif of M2-9.