Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
Light Echoes from V838 Mon
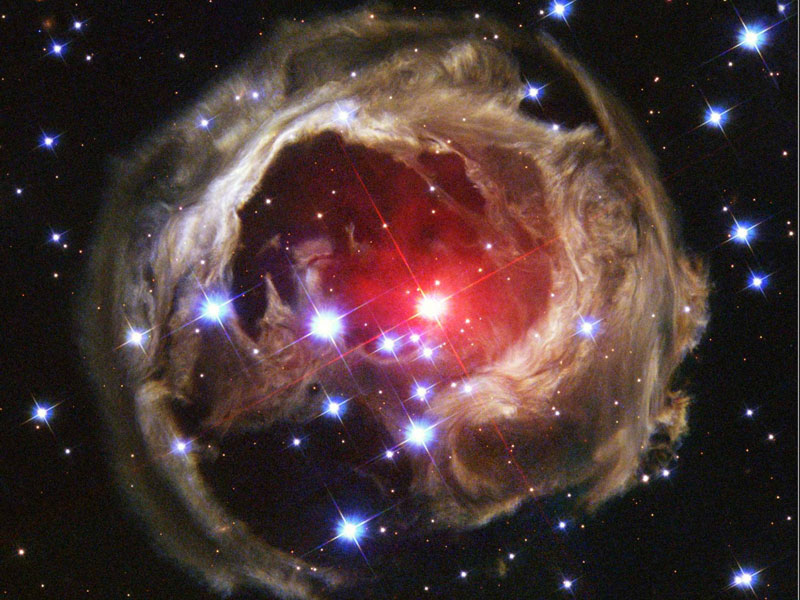

03/02/2008
Supernova Factory NGC 2770
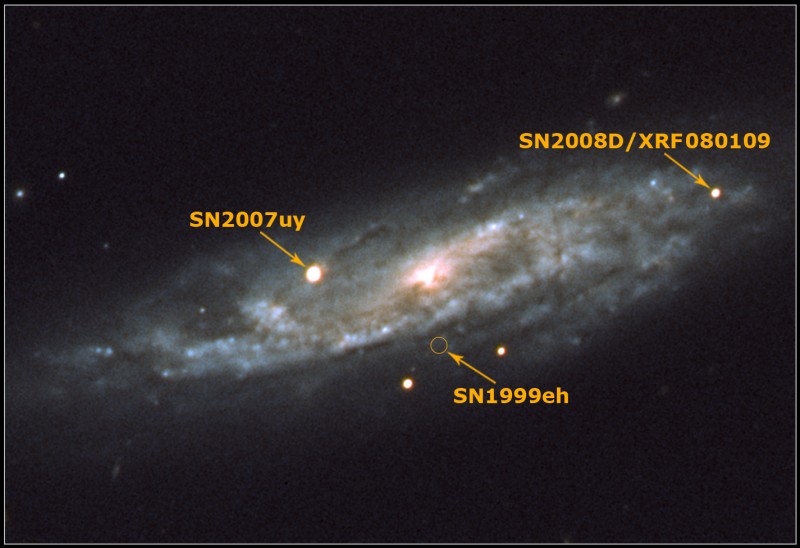

18/01/2008
Thor's Emerald Helmet
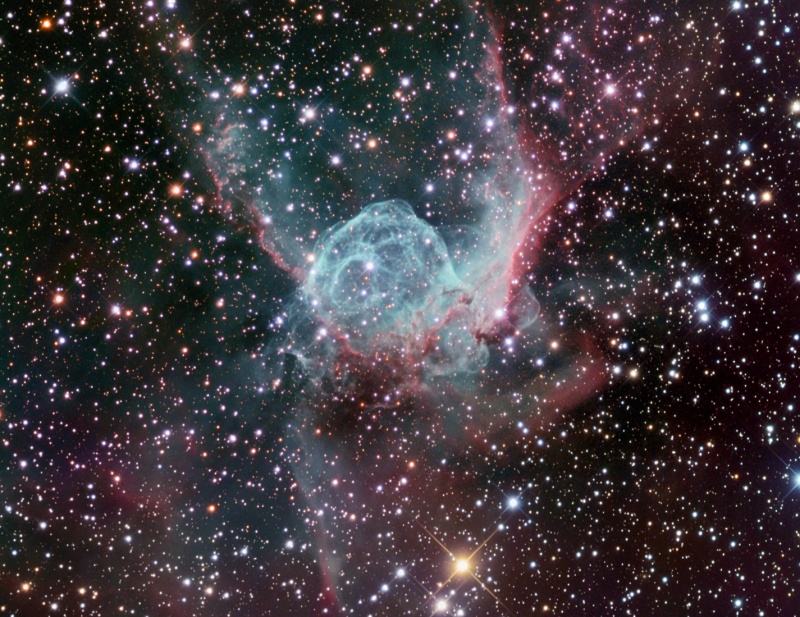

17/01/2008
Double Supernova Remnants DEM L316
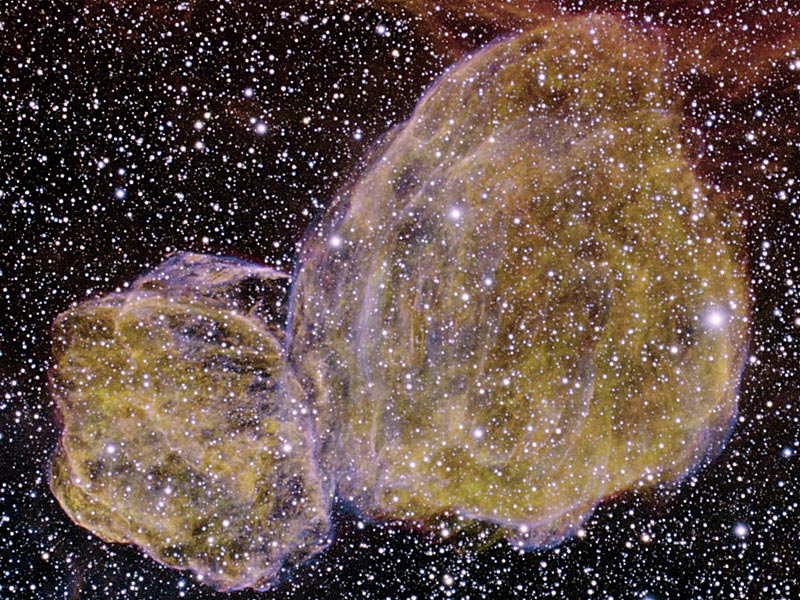

15/01/2008
NGC 6888: The Crescent Nebula
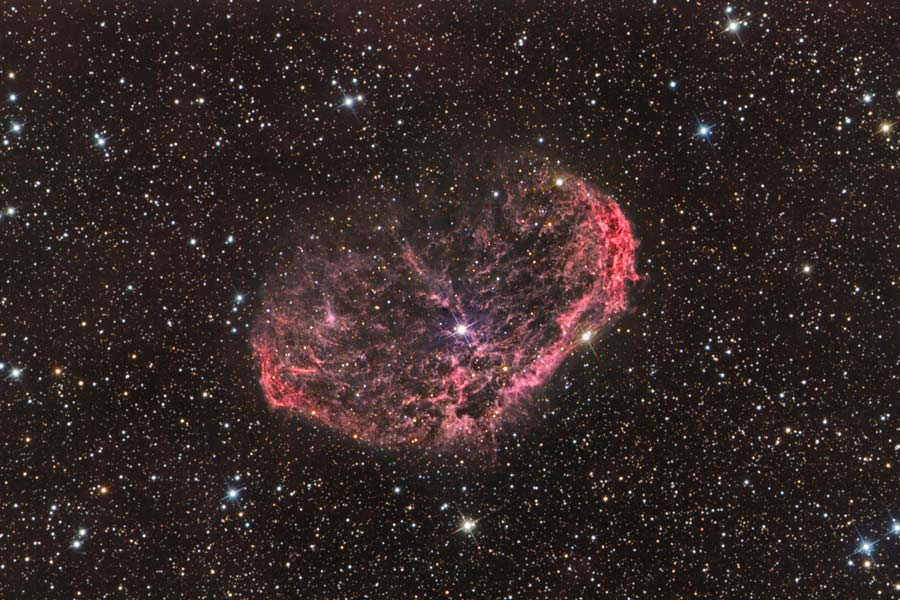

11/11/2007
SN 2005ap: The Brightest Supernova Yet Found
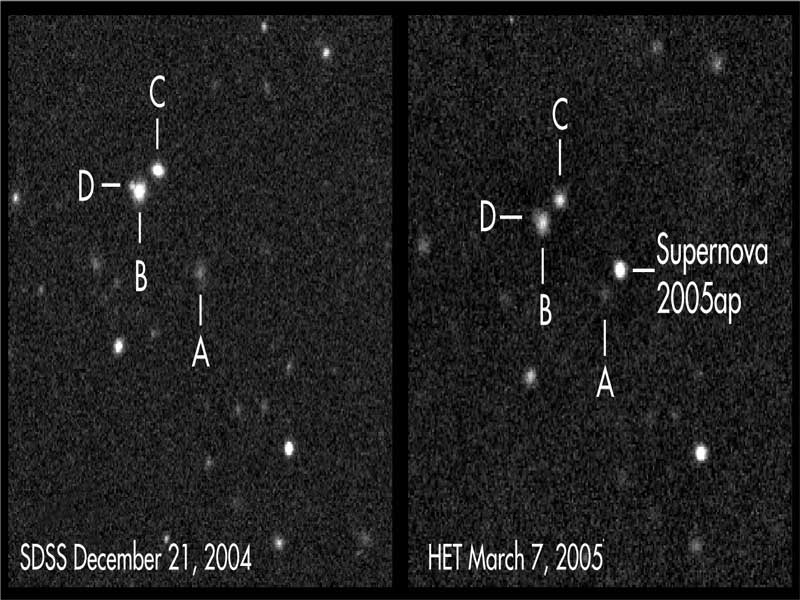
16/10/2007
A Galactic Star Forming Region in Infrared
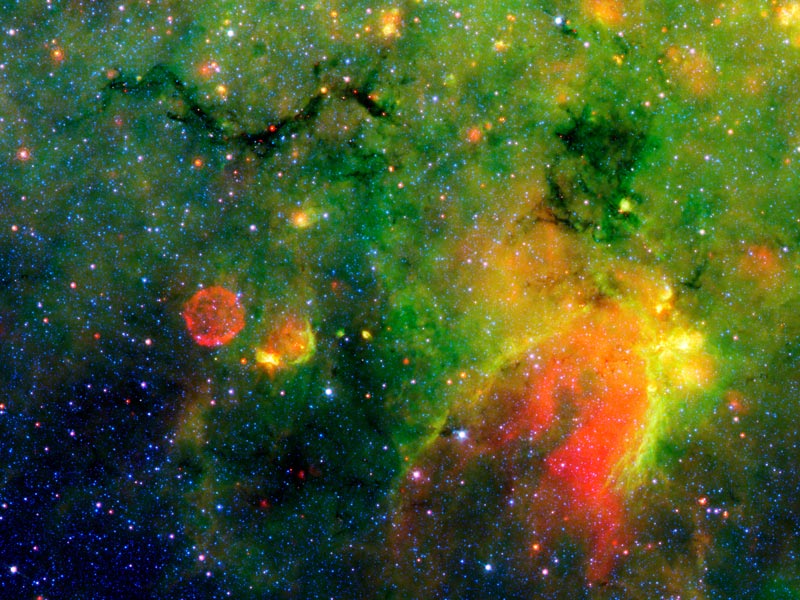

24/09/2007
Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
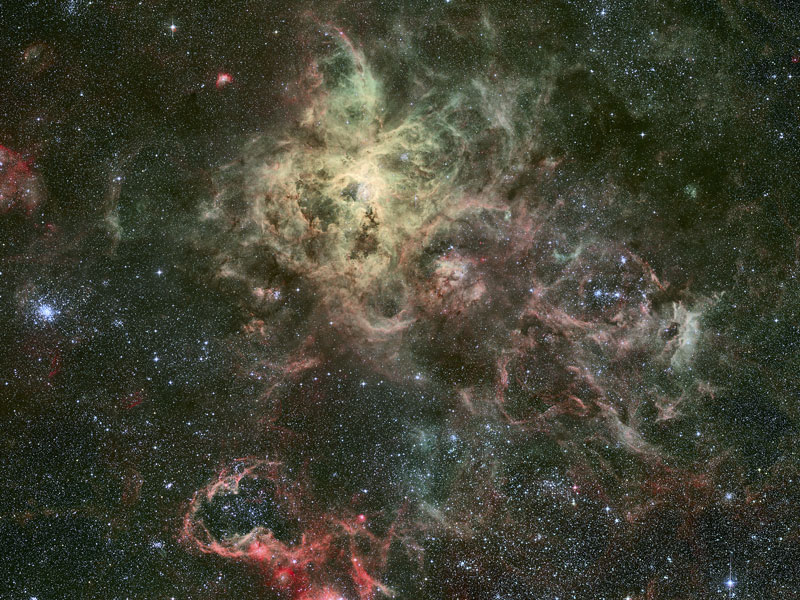

22/08/2007
The Trifid Nebula in Stars and Dust
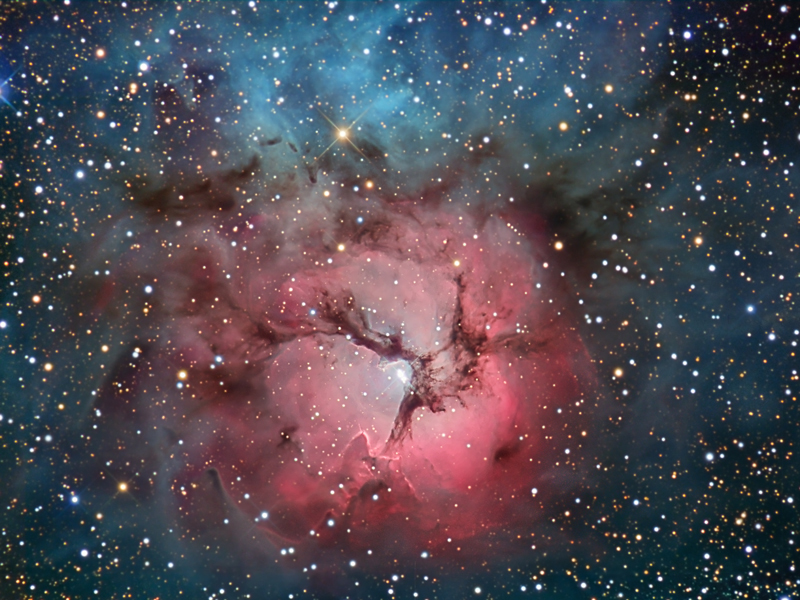

13/08/2007
Spiral Galaxy M83: The Southern Pinwheel
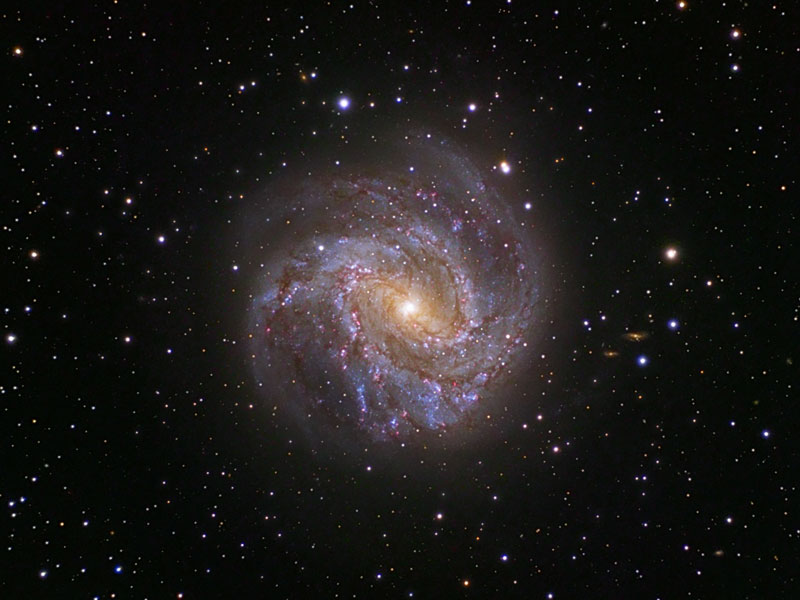

24/07/2007
The Lagoon Nebula in Gas, Dust, and Stars

16/07/2007
SN 2006GY: Brightest Supernova
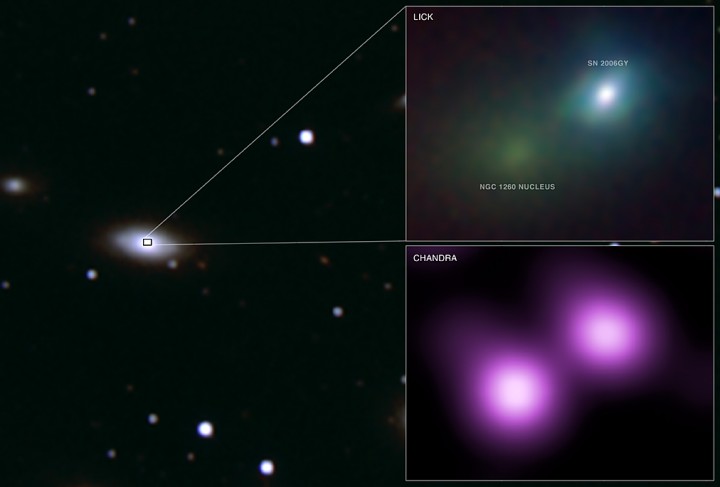

10/05/2007
MWC 922: The Red Square Nebula
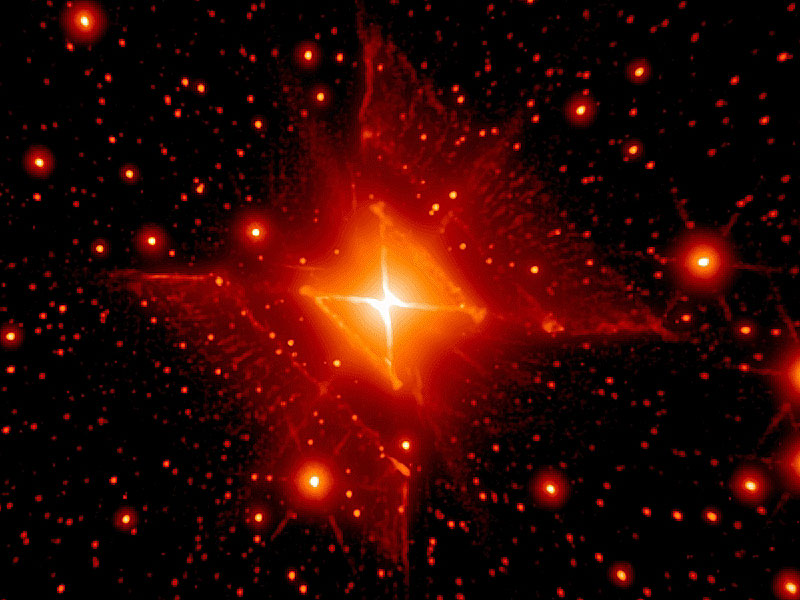

16/04/2007
Barred Spiral Galaxy M95
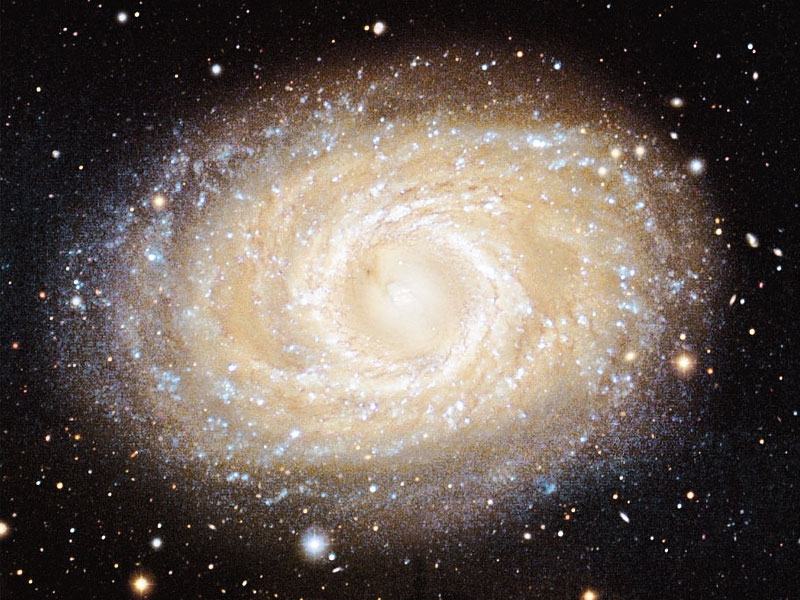

14/03/2007
Vela Supernova Remnant in Visible Light
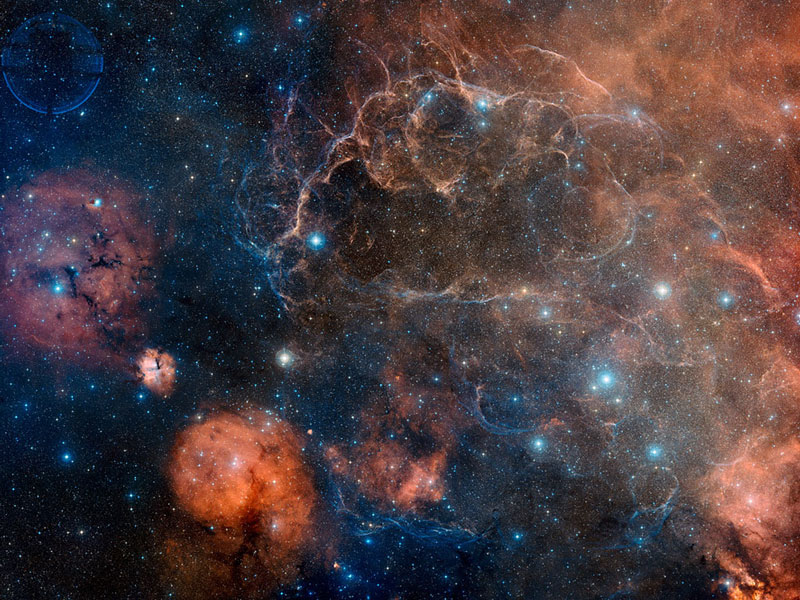

13/02/2007
Kepler's Supernova Remnant in X-Rays
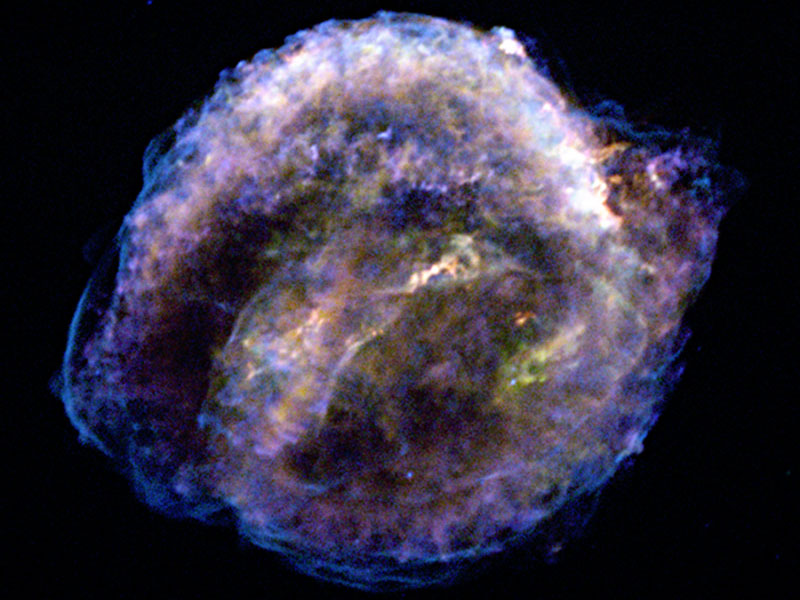
16/01/2007
The Eagle Nebula in Infrared
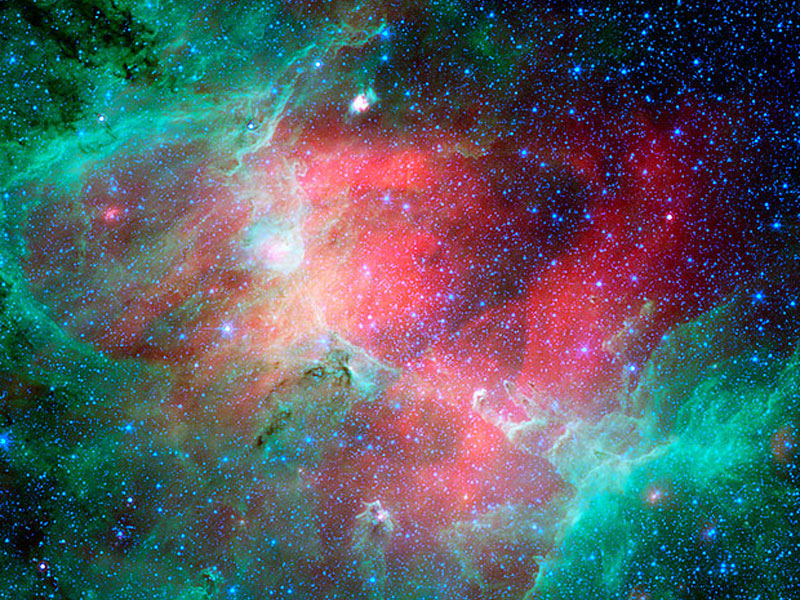

11/01/2007
The Mysterious Rings of Supernova 1987A
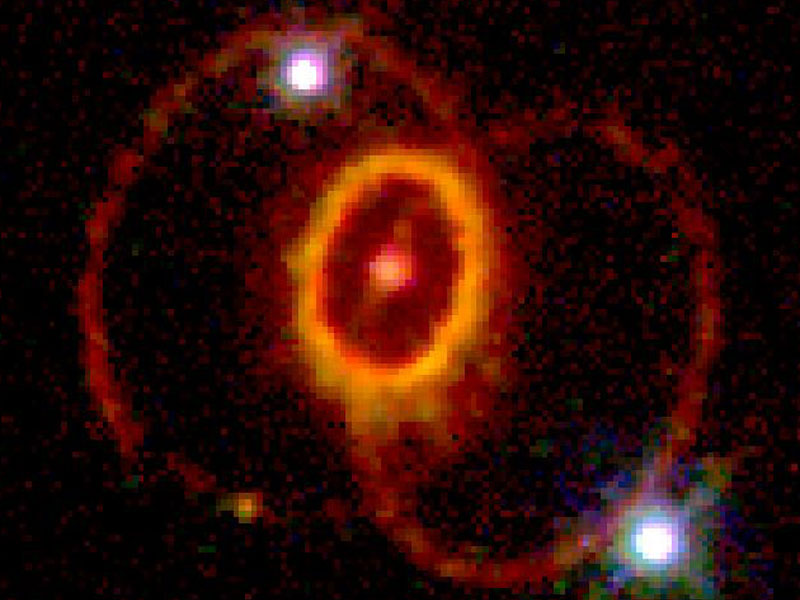

07/01/2007
NGC 6960: The Witch's Broom Nebula
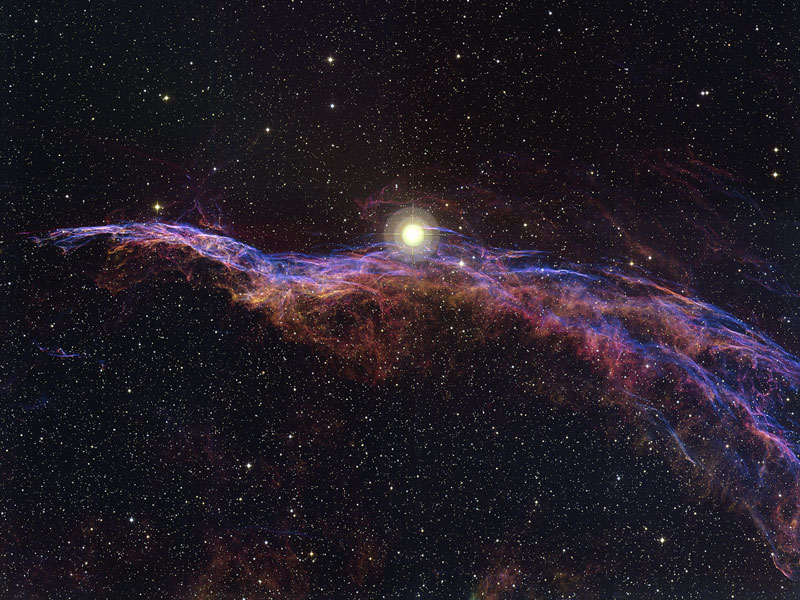

01/01/2007
Rumors of a Strange Universe
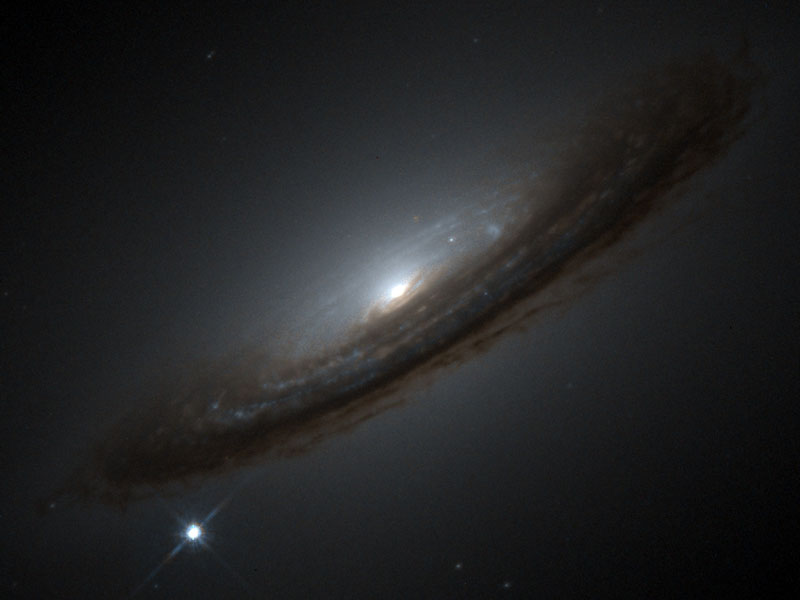

24/12/2006
Alpha Cam: Runaway Star
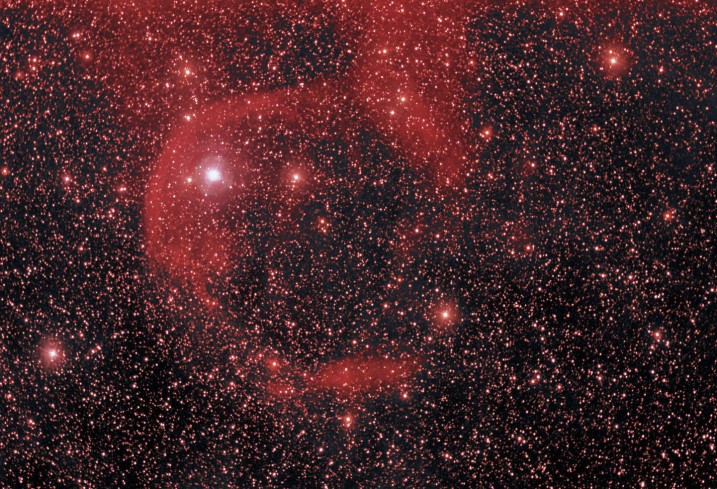

24/11/2006
Composite Crab
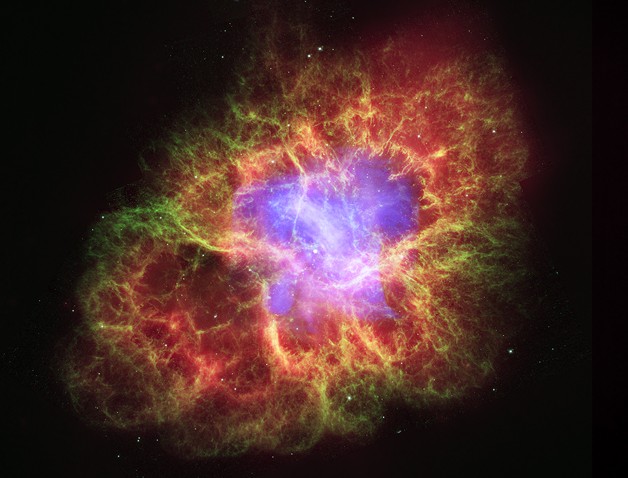

26/10/2006
RCW 86: Historical Supernova Remnant
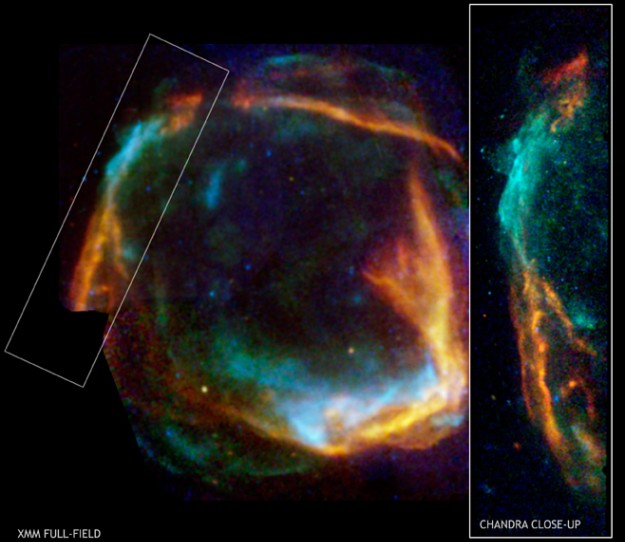

28/09/2006
Supernova Remnant E0102 from Hubble
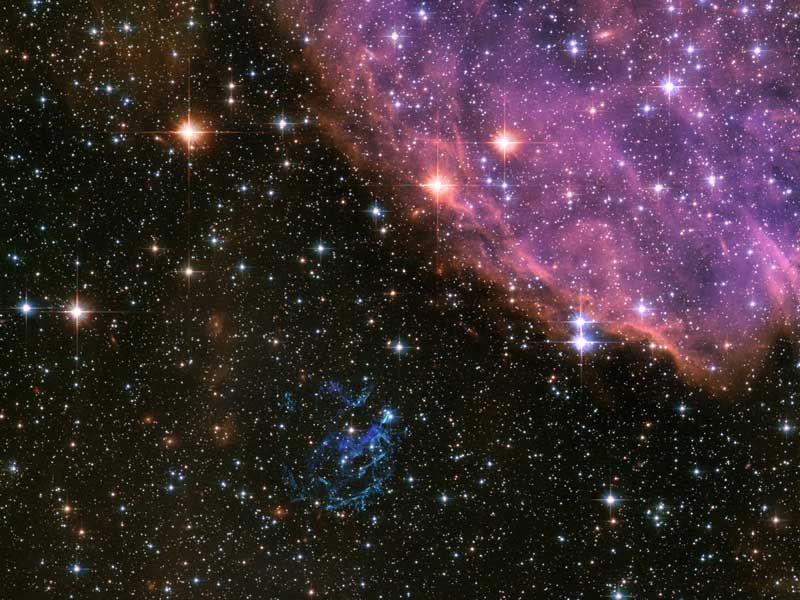

29/08/2006
Four Supernova Remnants

28/07/2006
Explosions from White Dwarf Star RS Oph
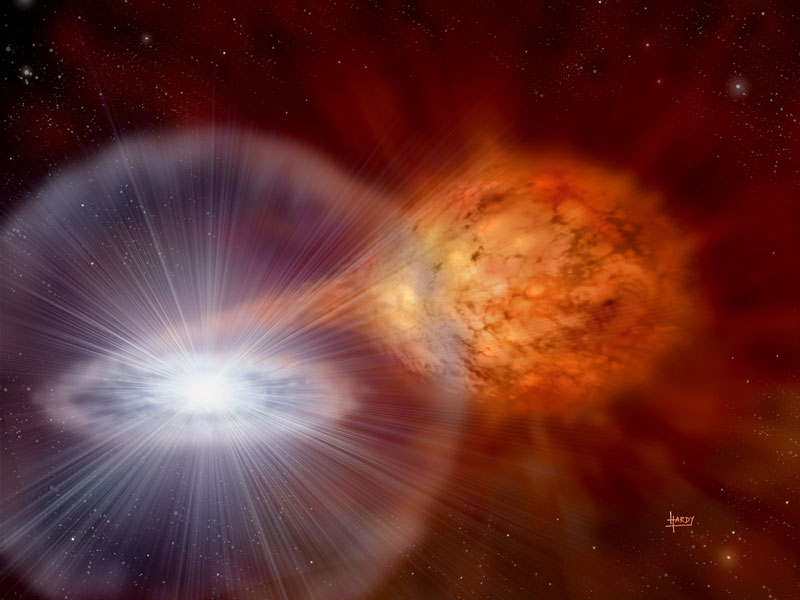

26/07/2006
Bright Galaxy M81
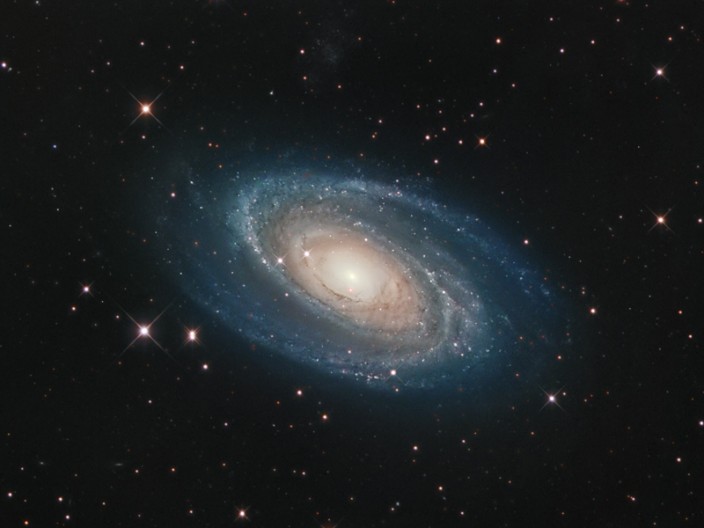

07/07/2006
NGC 6888: A Tricolor Starfield
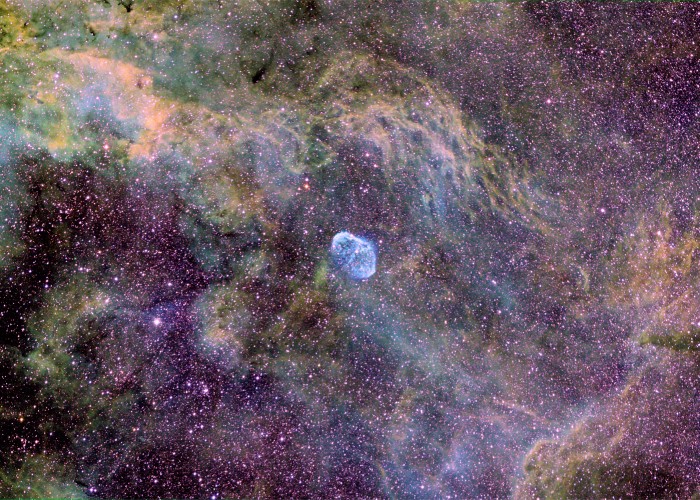

06/07/2006
Spiral Galaxy NGC 2403 from Subaru
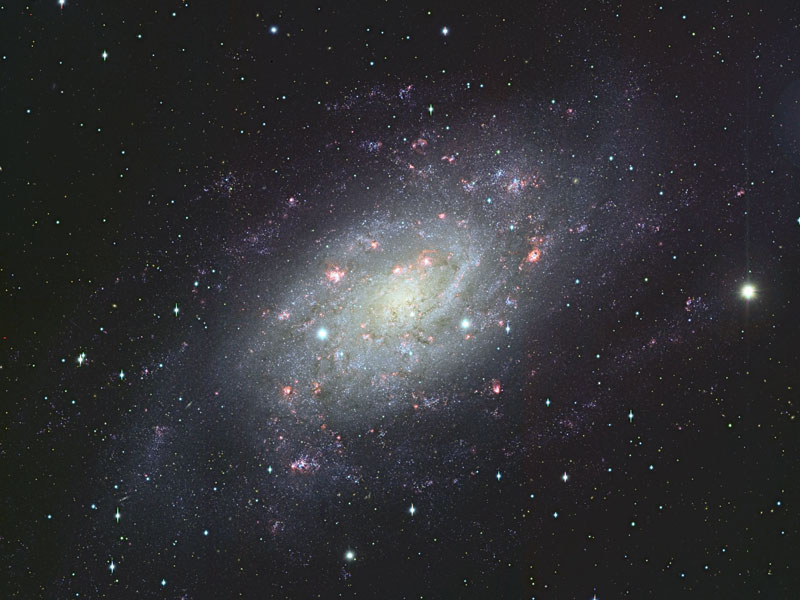

05/07/2006
Gamma-Ray Earth
03/06/2006