Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
IC 443: Supernova Remnant and Neutron Star
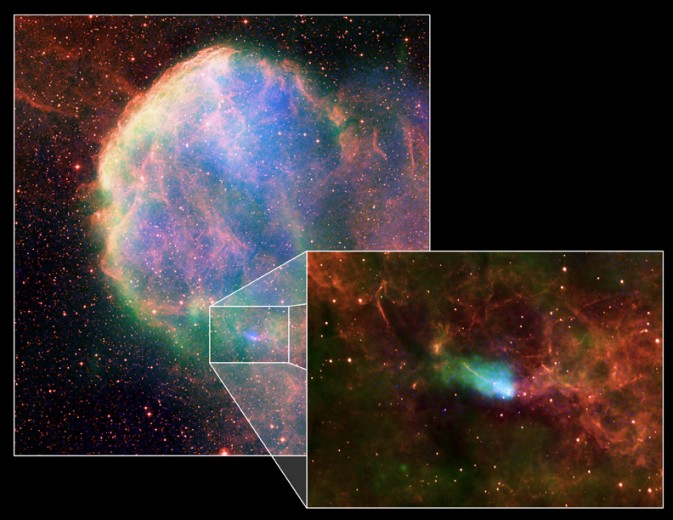

02/06/2006
Reflections on NGC 6188
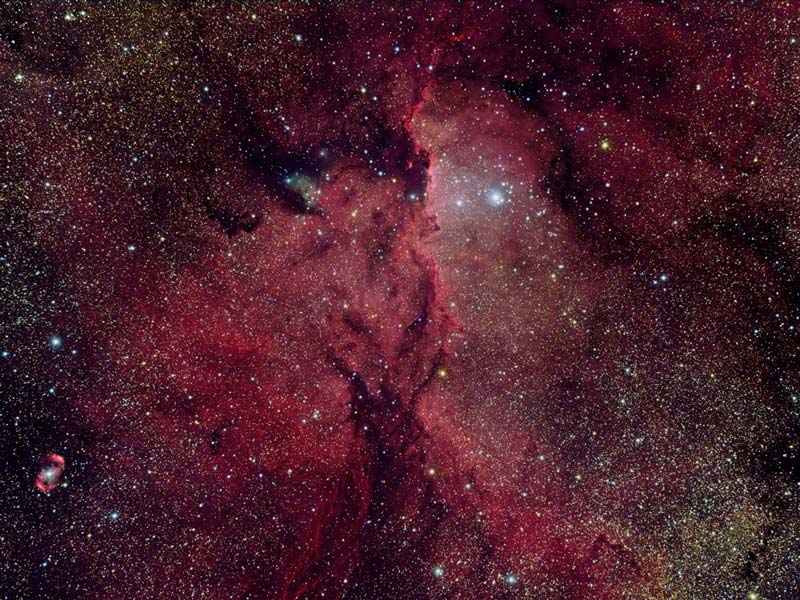

01/06/2006
The Gum Nebula
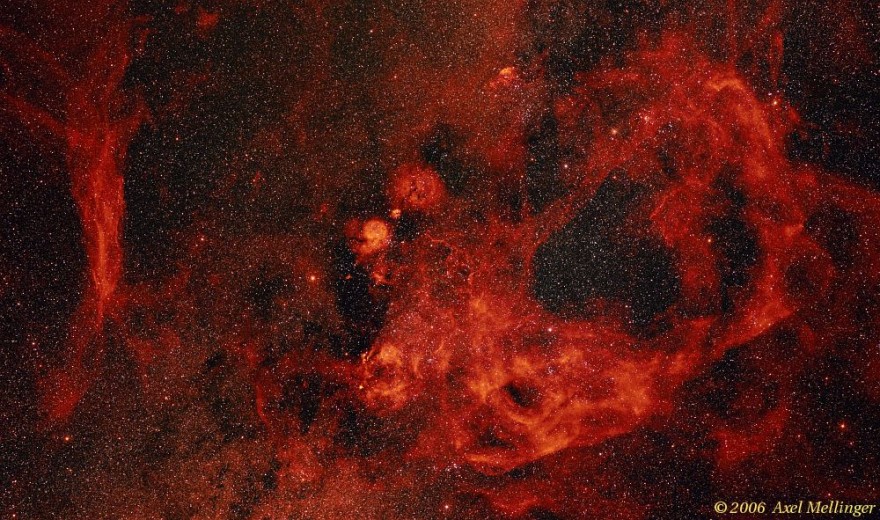

19/05/2006
The Host Galaxies of Long-Duration GRBs
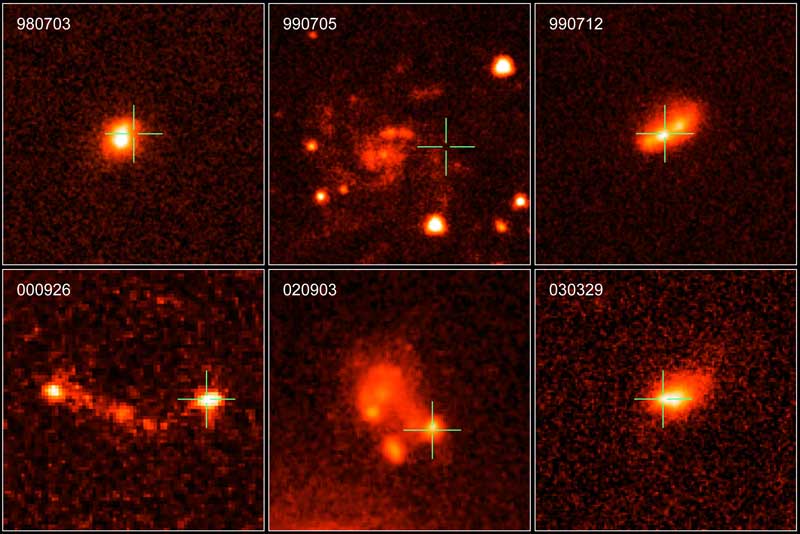

17/05/2006
The Large Cloud of Magellan
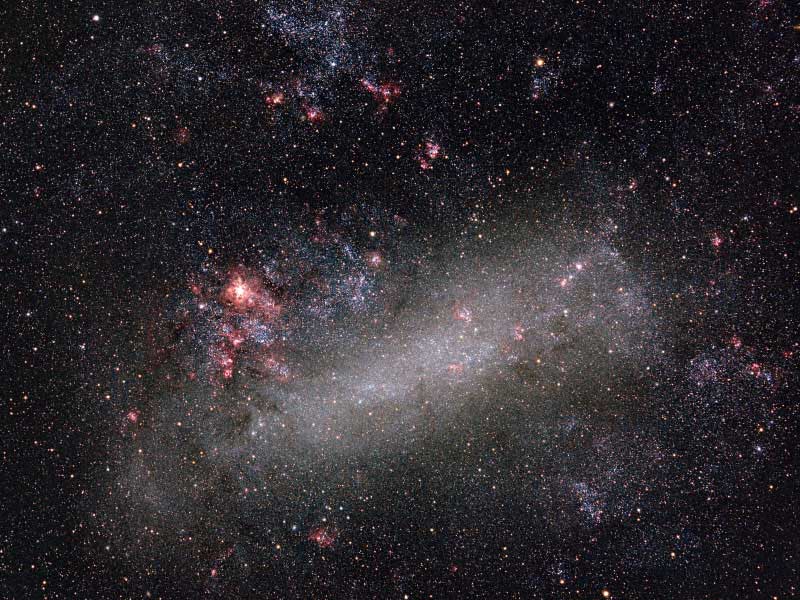

10/05/2006
1006 AD: Supernova in the Sky

30/04/2006
Barnard's Loop around the Horsehead Nebula
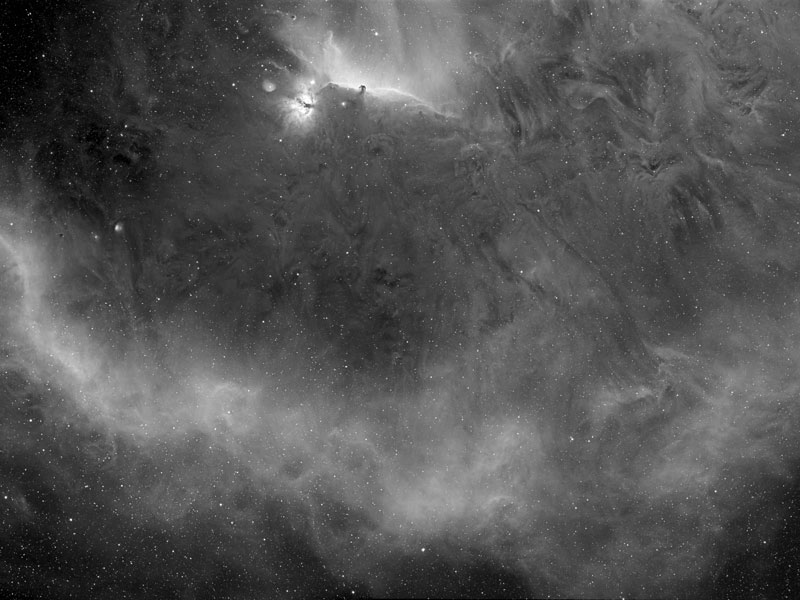

17/04/2006
Doomed Star Eta Carinae
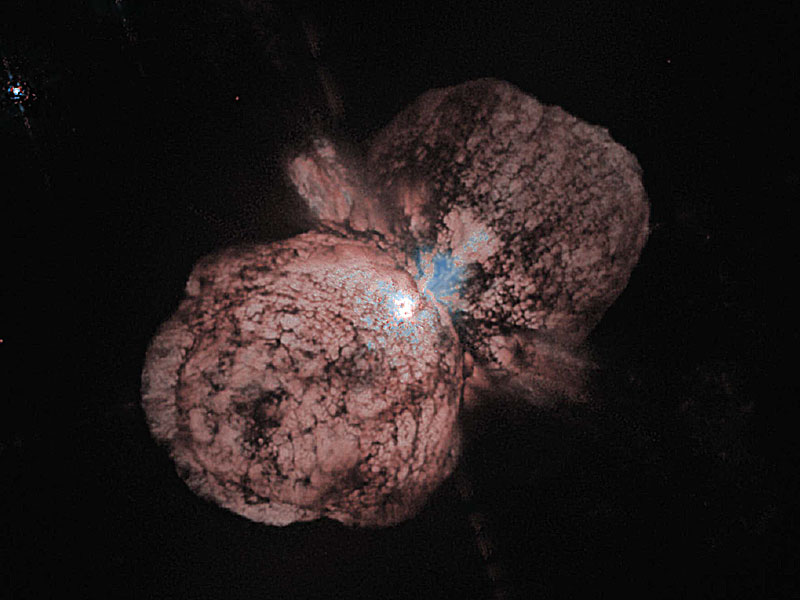

26/03/2006
A Nearby Supernova in Spiral Galaxy M100
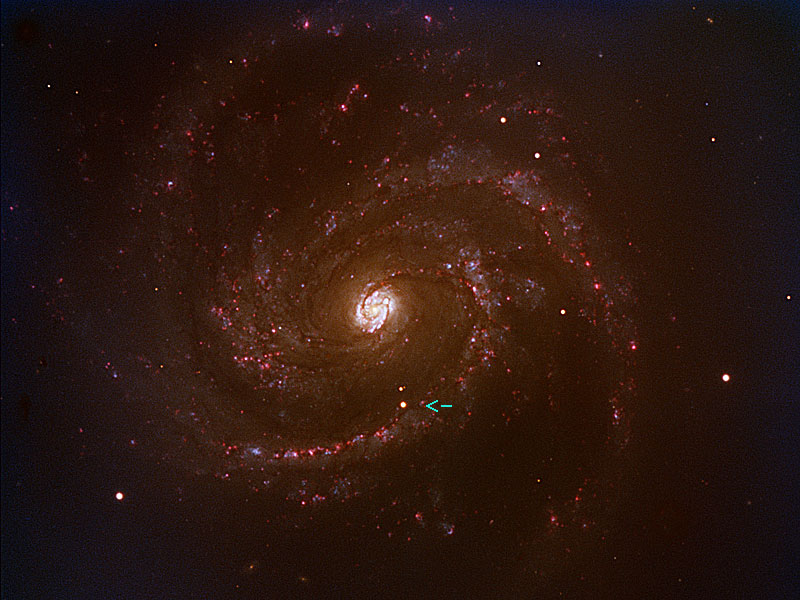

07/03/2006
GRB 060218: A Mysterious Transient

27/02/2006
Wisps Surrounding the Horsehead Nebula
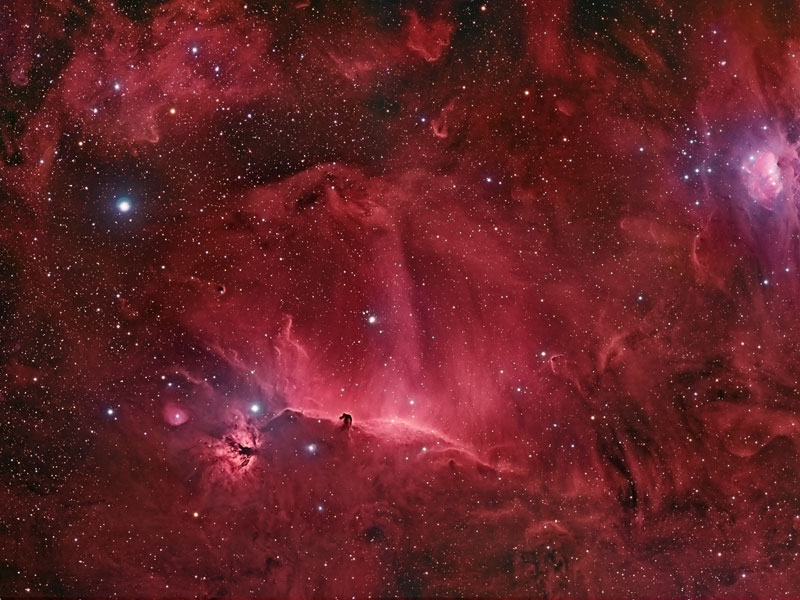

21/02/2006
Supernova Remnant and Shock Wave
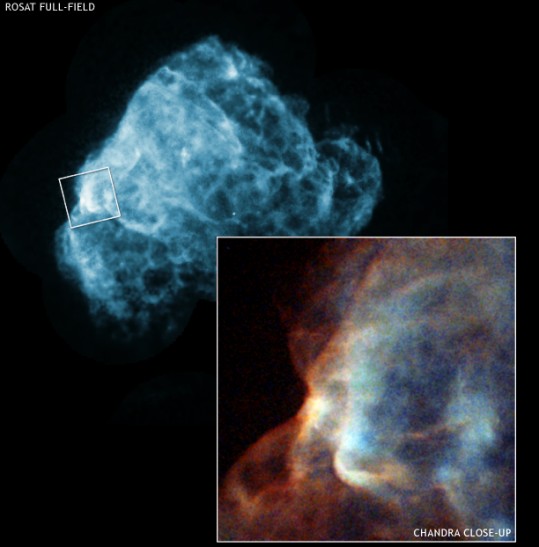
17/02/2006
NGC 1309 and Friends
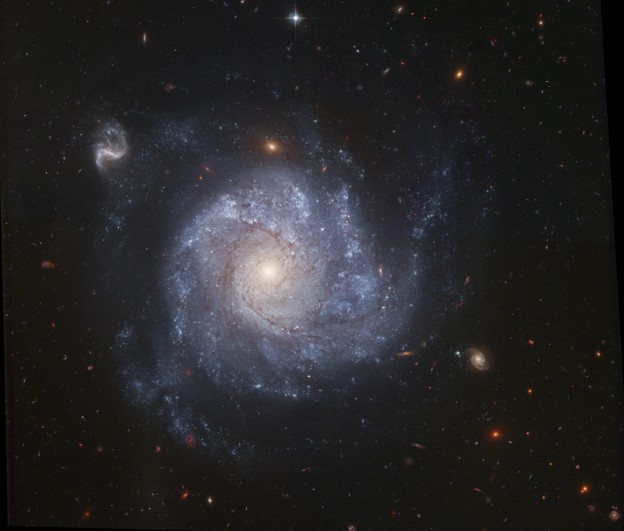

09/02/2006
The N44 Superbubble
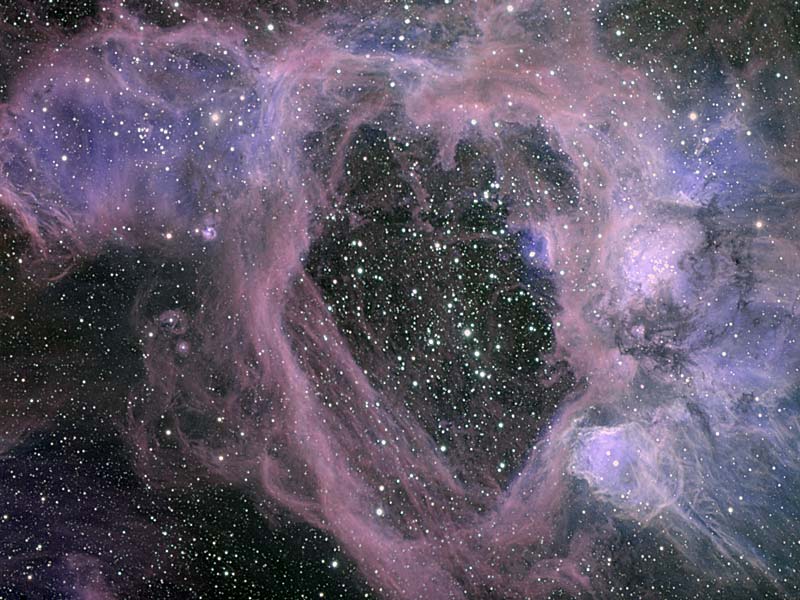

06/02/2006
Thor's Helmet in H-Alpha
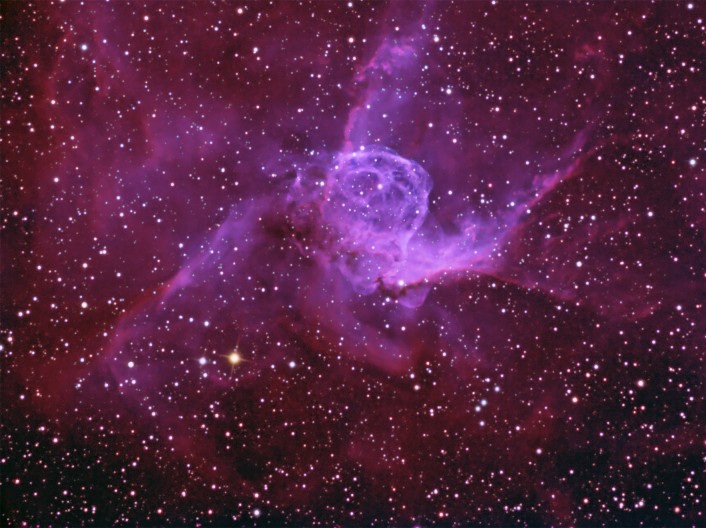

02/02/2006
The Expanding Light Echoes of SN 1987A
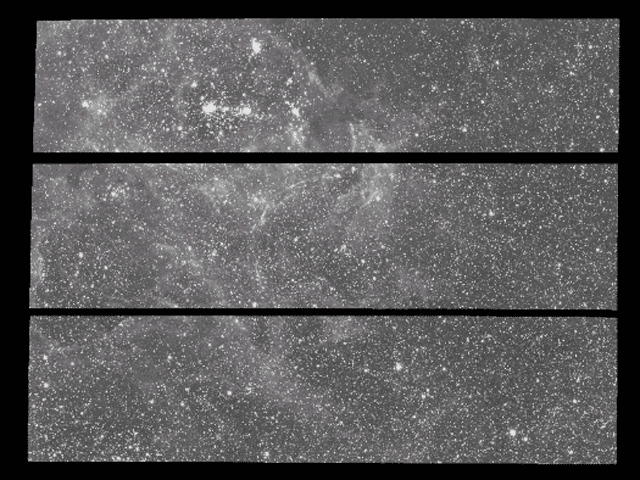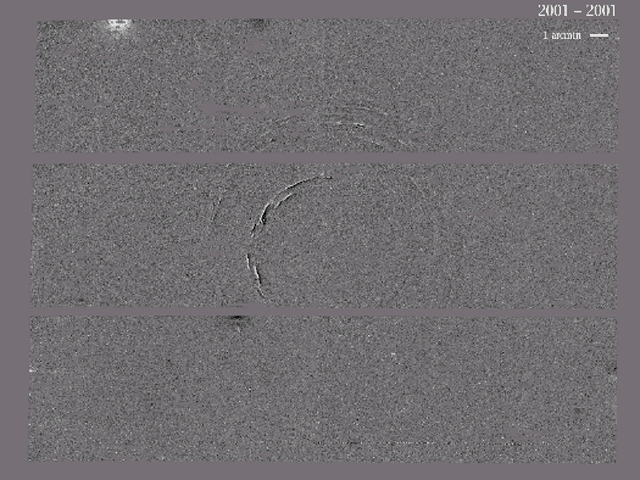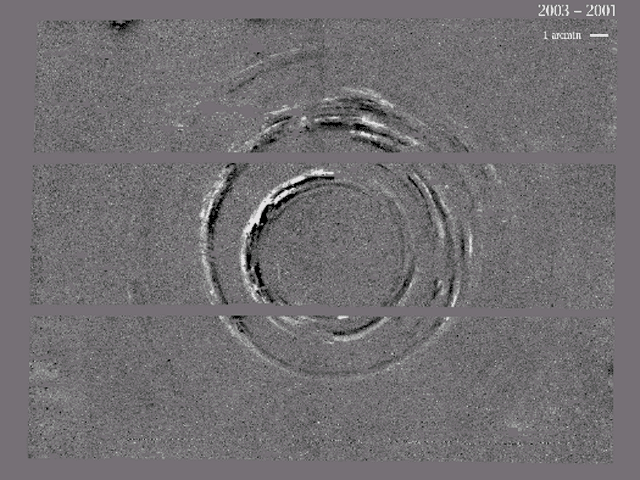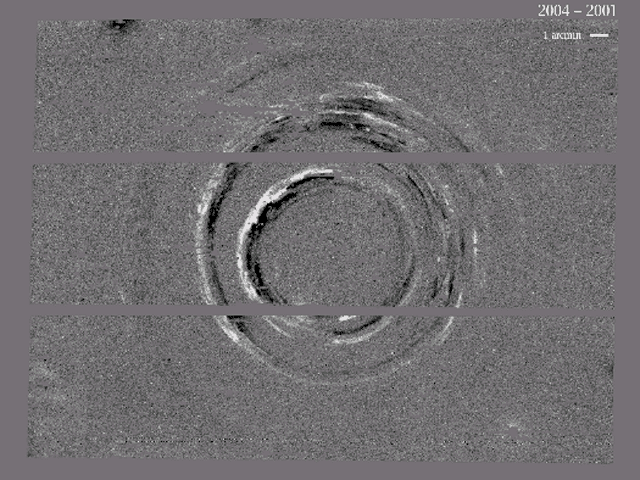
25/01/2006
The LMC Galaxy in Glowing Gas
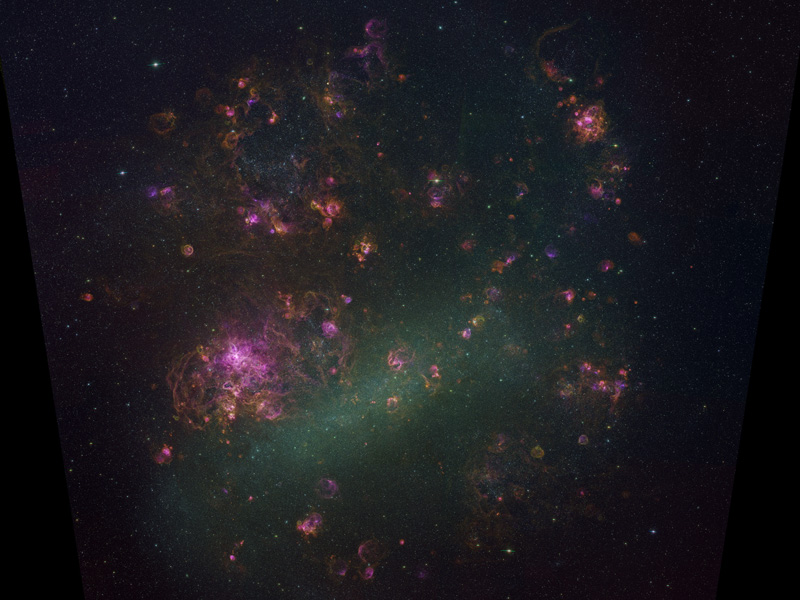

23/01/2006
The Tarantula Nebula
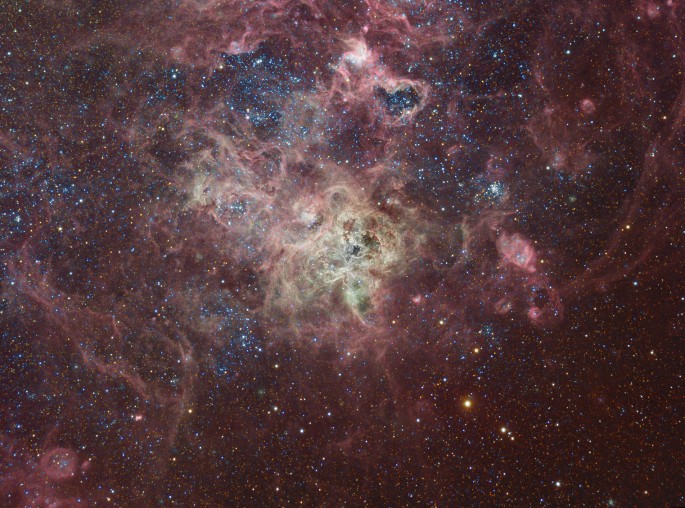

06/01/2006
SN 1006: Supernova Remnant in X-Rays
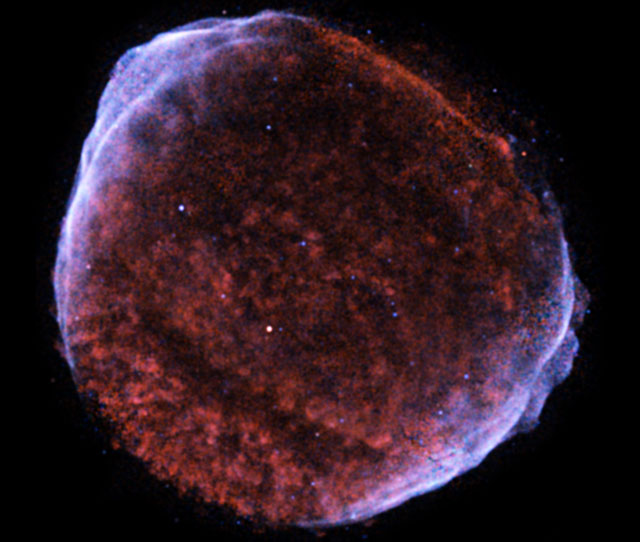
26/12/2005
M83: The Southern Pinwheel Galaxy from VLT
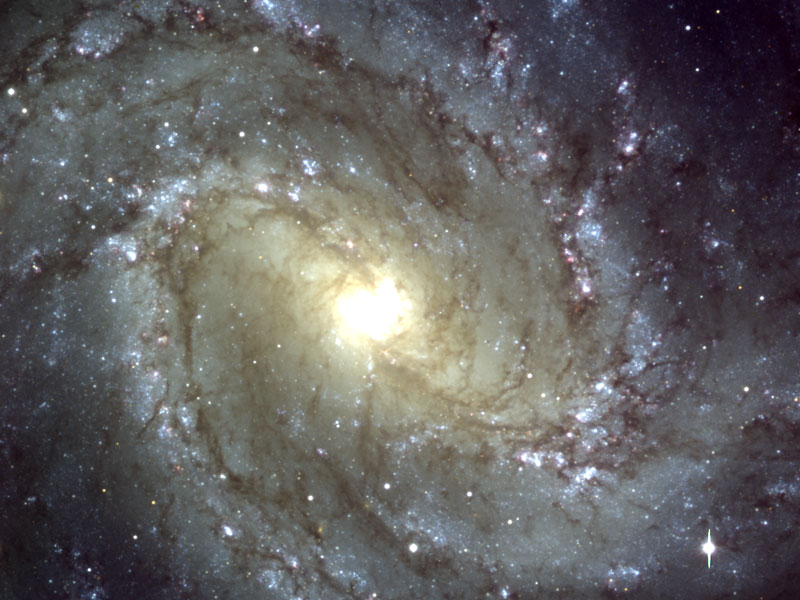

18/12/2005
30 Doradus: The Tarantula Zone
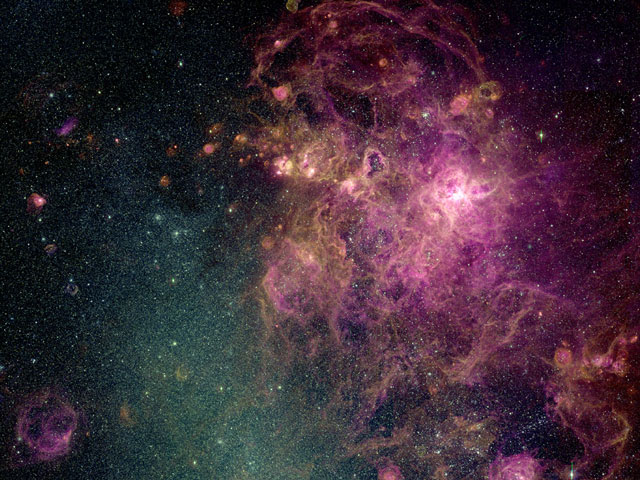

12/12/2005
The Veil Nebula Unveiled

06/12/2005
Crab Nebula Mosaic from HST
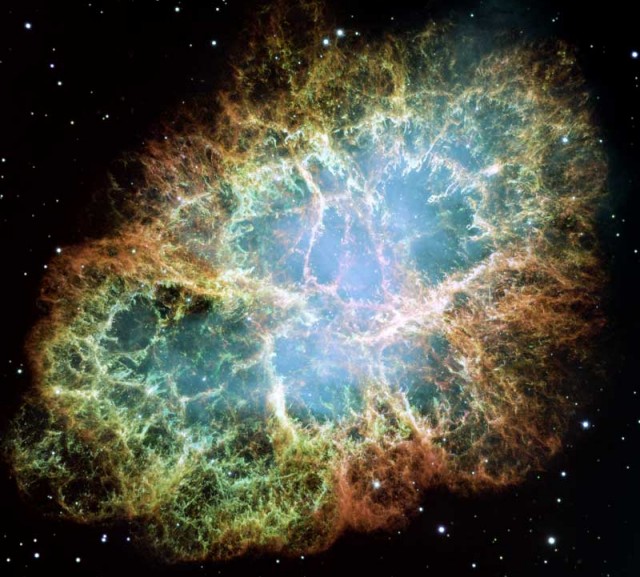
02/12/2005
Simeis 147: Supernova Remnant from Palomar
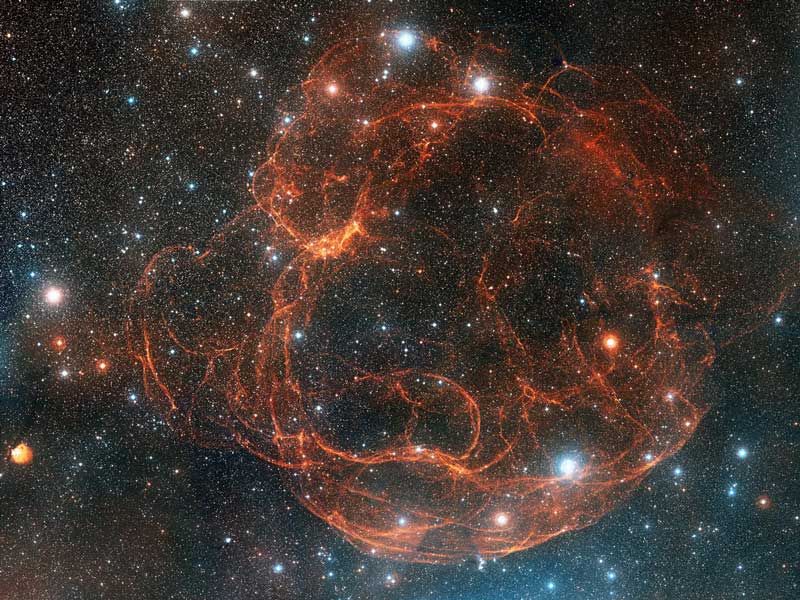

29/11/2005
Light Echoes from V838 Mon
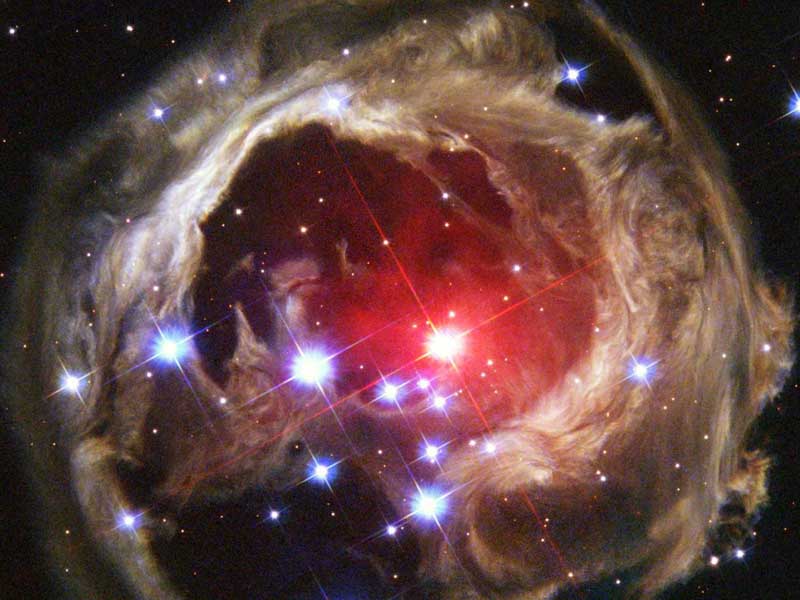

27/11/2005
Supernova Remnant N132D in Optical and X Rays
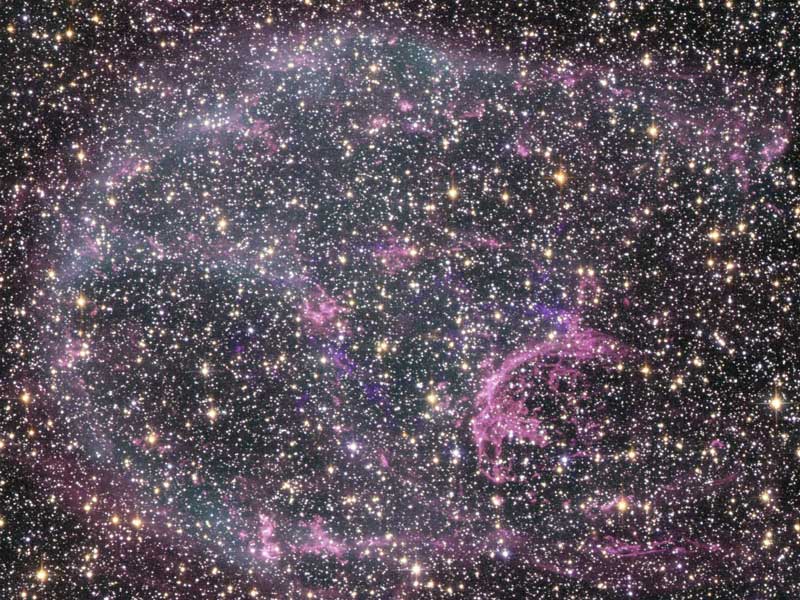

25/10/2005
Dusty Environs of Eta Carinae
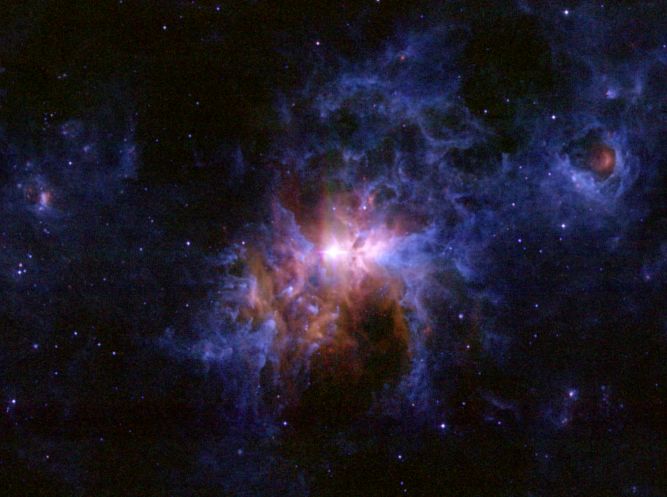

15/10/2005
M1: The Crab Nebula from NOT
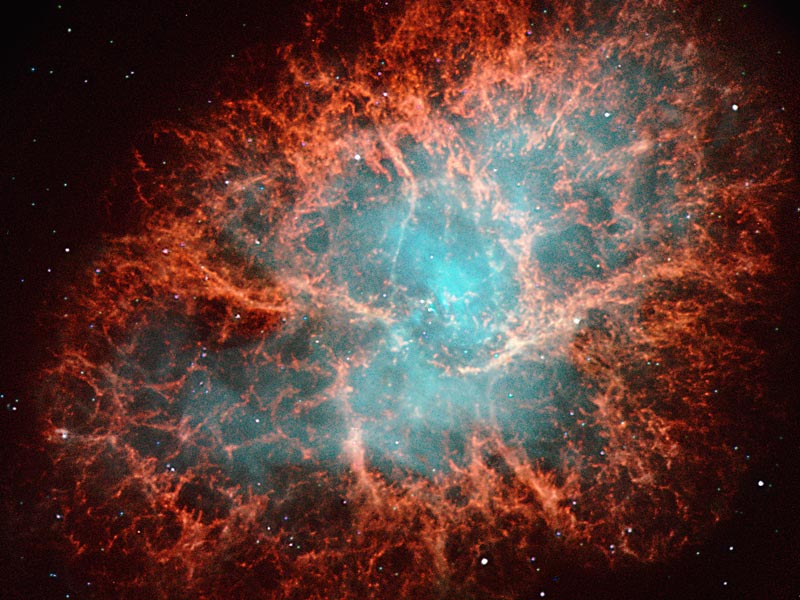

20/09/2005
Supernova Survivor
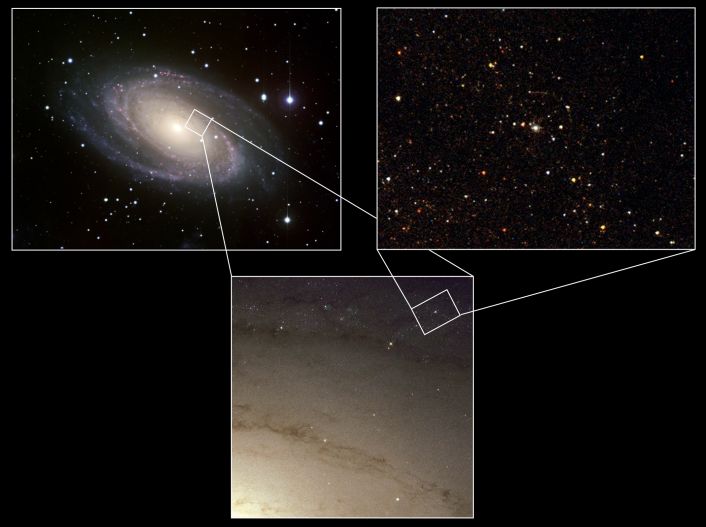

10/09/2005
X-Ray Portrait of Trumpler 14
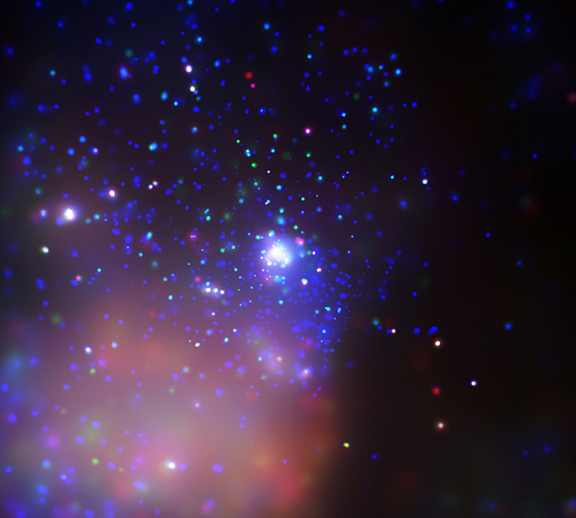

02/09/2005