Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
SNR 0103-72.6: Oxygen Supply
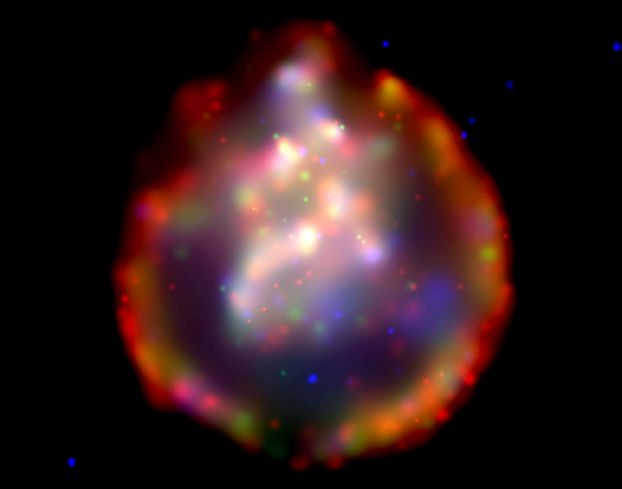
13/08/2005
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
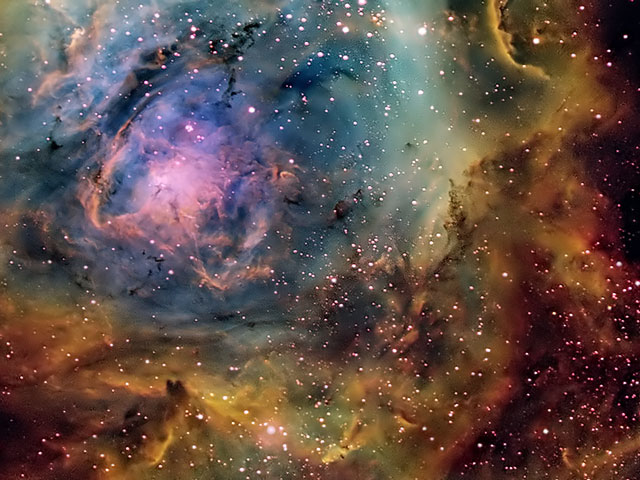

03/08/2005
A Nearby Supernova in M51
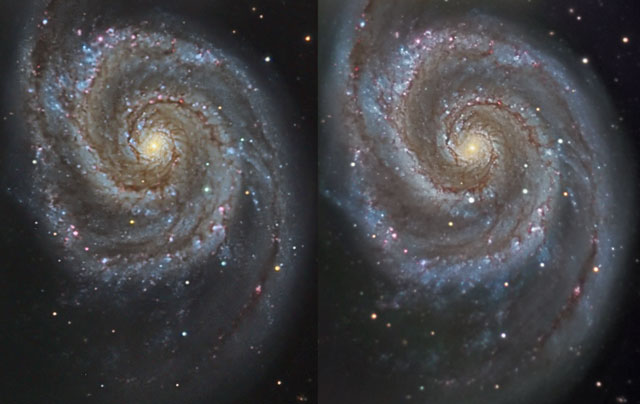

19/07/2005
Cassiopeia A Light Echoes in Infrared
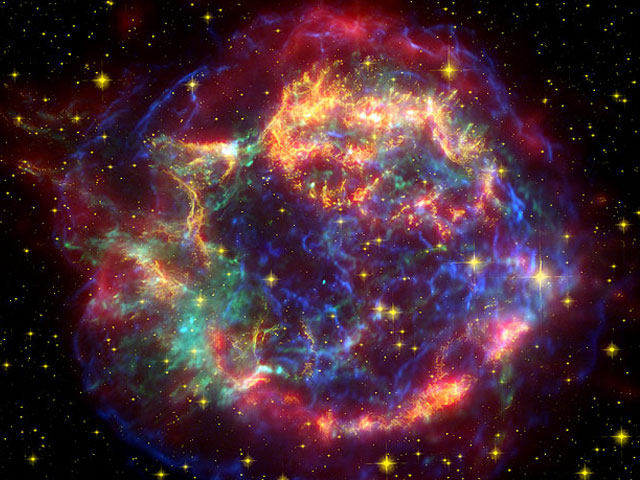
15/06/2005
Rampaging Supernova Remnant N63A
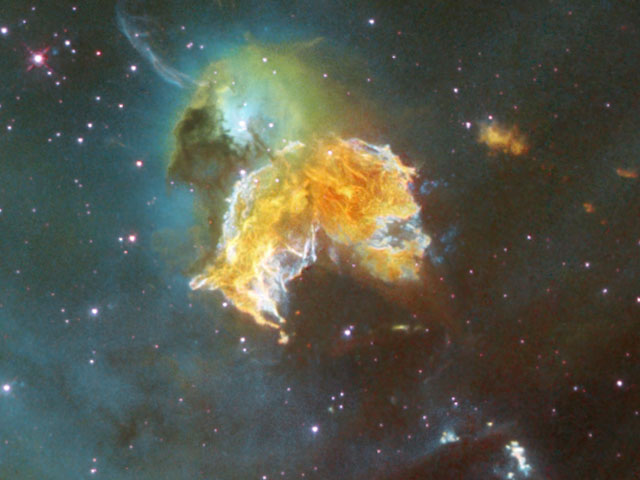

08/06/2005
The Trifid Nebula from CFHT

31/05/2005
On the Origin of Gold
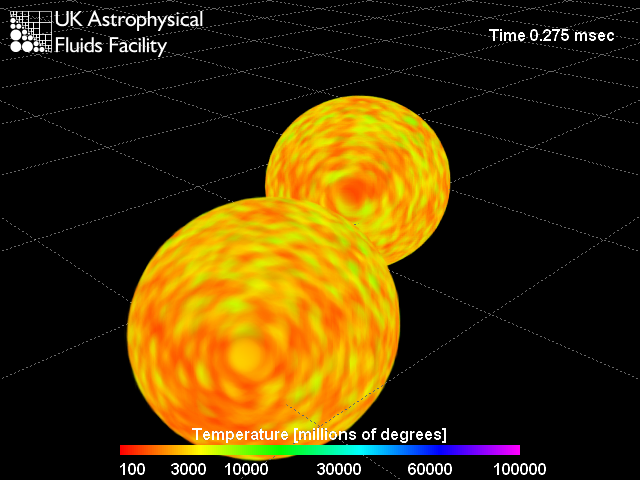
15/05/2005
NGC 3370: A Sharper View
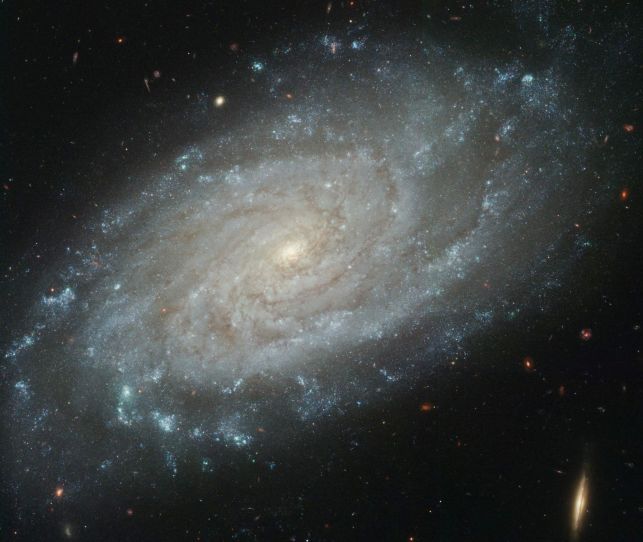

14/05/2005
G21.5-0.9: A Supernova's Cosmic Shell

21/04/2005
Barnard's Loop Around Orion
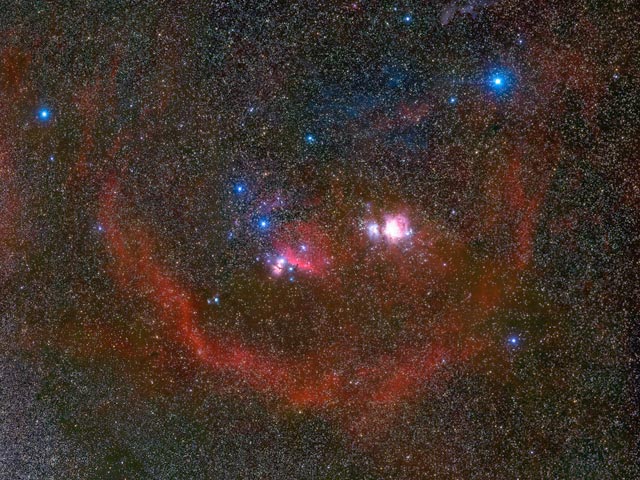

20/04/2005
Cyg X-1: Can Black Holes Form in the Dark?
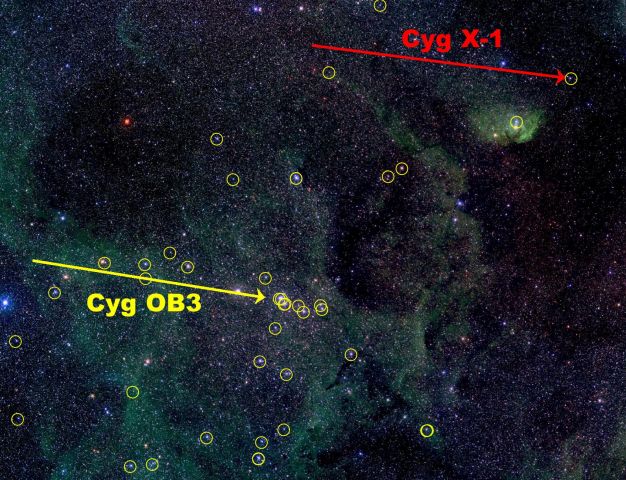
02/04/2005
Gamma-Ray Earth
31/03/2005
Composite Crab
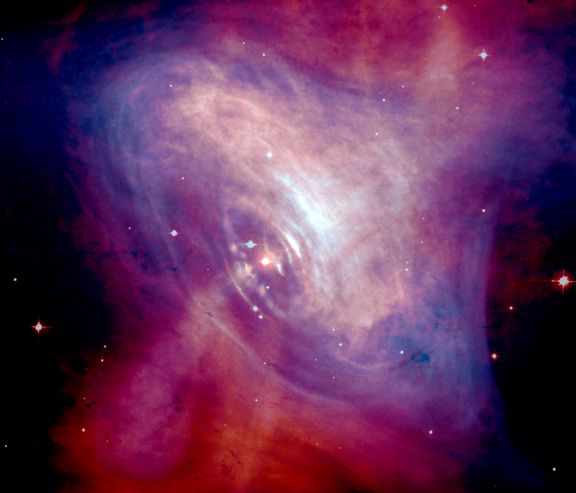

26/03/2005
Simeis 147: Supernova Remnant
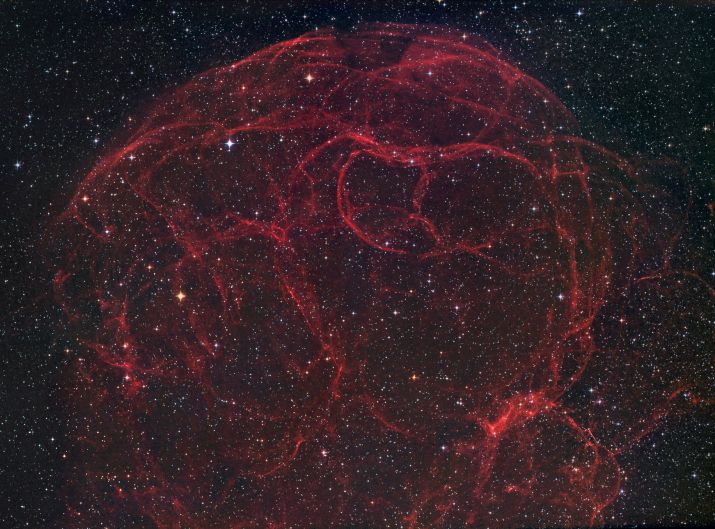

24/03/2005
Galactic Magnetar Throws Giant Flare
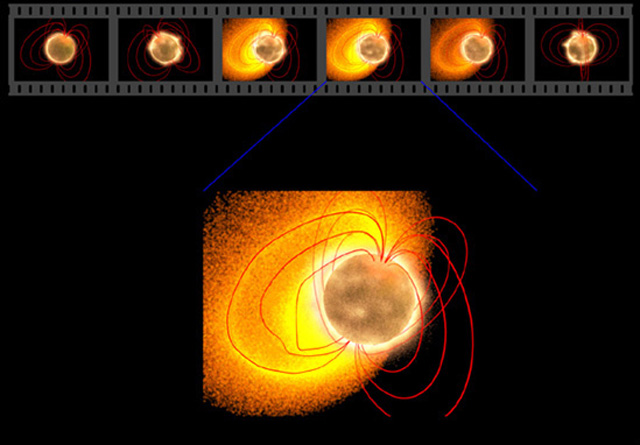
21/02/2005
The Radio Sky: Tuned to 408MHz
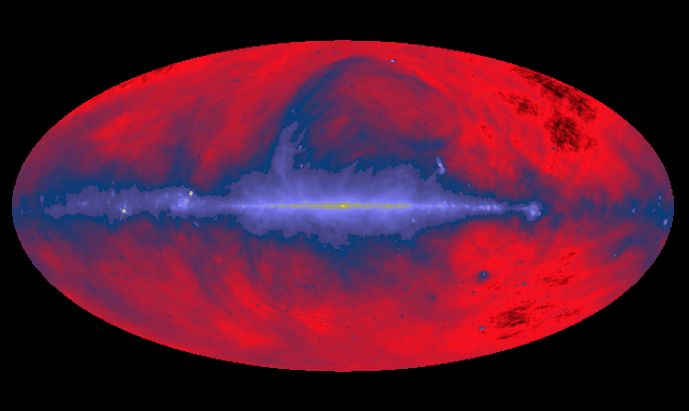
05/02/2005
NGC 6946: The Fireworks Galaxy

25/01/2005
X-Ray Mystery in RCW 38
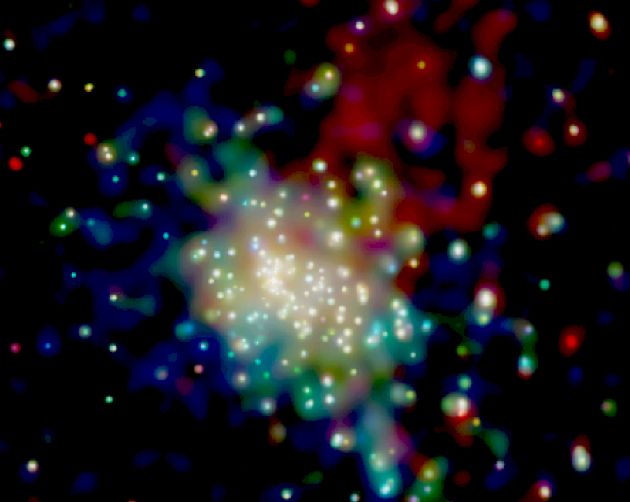

08/01/2005
M81 and M82: GALEX Full Field
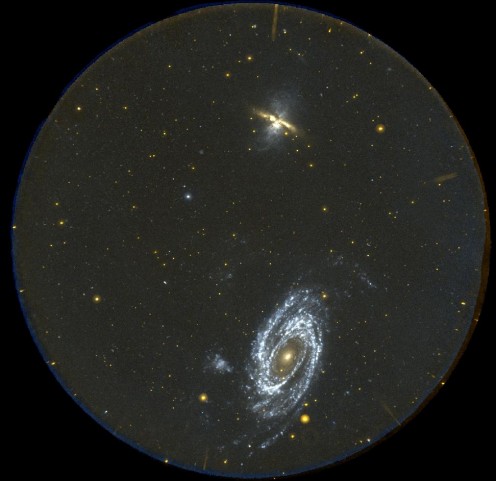

30/12/2004
3C58: Pulsar Power
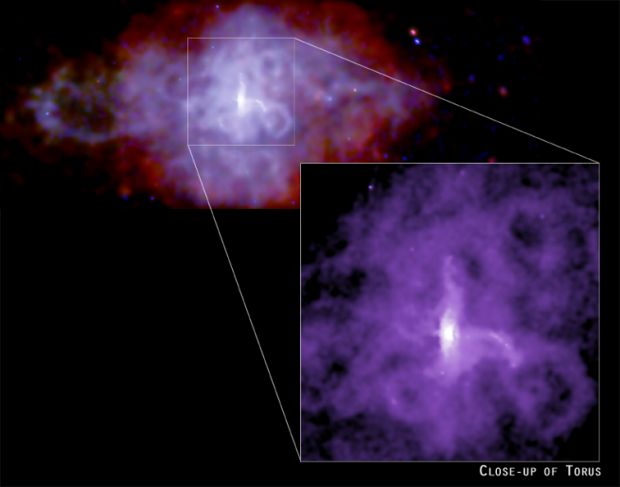
23/12/2004
The Arms of NGC 7424
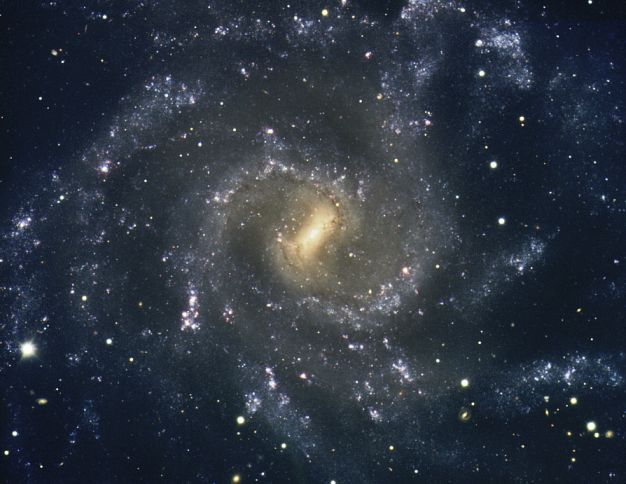

16/12/2004
Doomed Star Eta Carinae
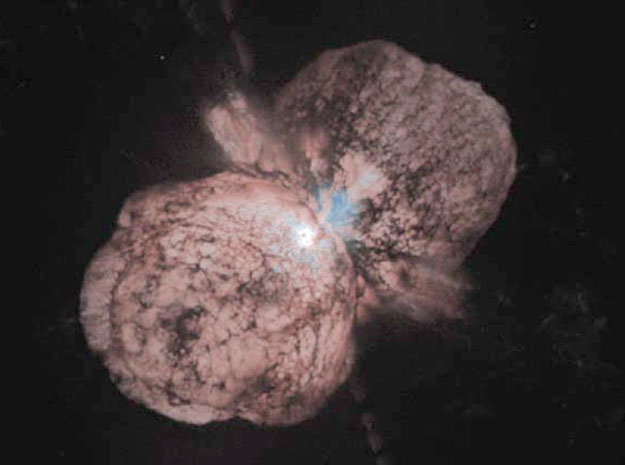
28/11/2004
What the Hubble Saw

25/11/2004
Supernova Remnant Imaged in Gamma Rays
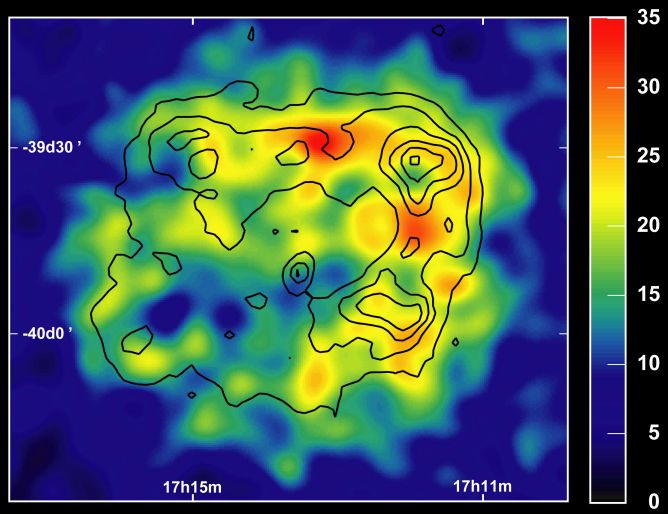
05/11/2004
Kepler's SNR from Chandra, Hubble, and Spitzer
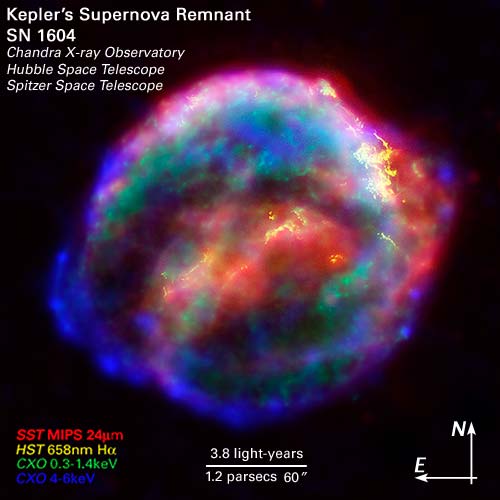
08/10/2004
Microquasar in Motion

16/09/2004
A Supernova in Nearby Galaxy NGC 2403
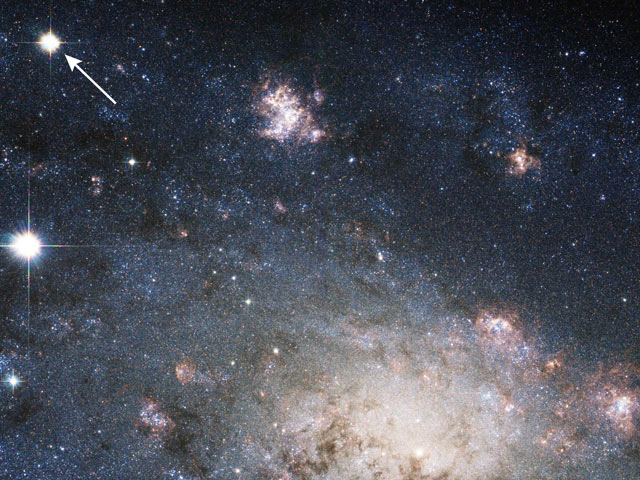

07/09/2004
The Large Cloud of Magellan
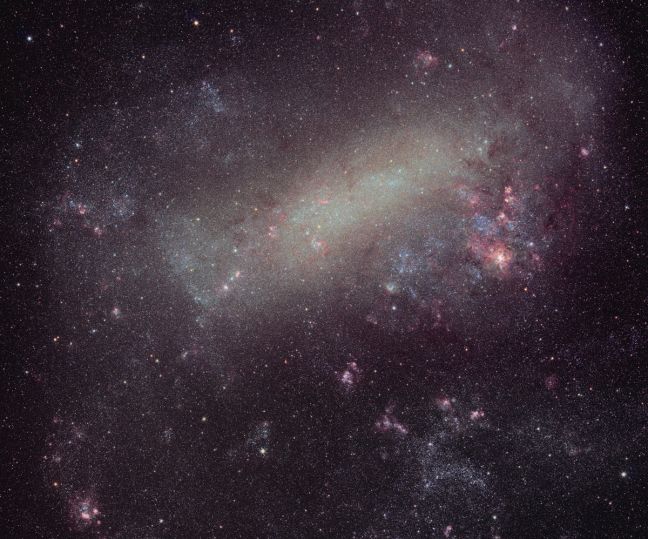

02/09/2004
Cassiopeia A in a Million
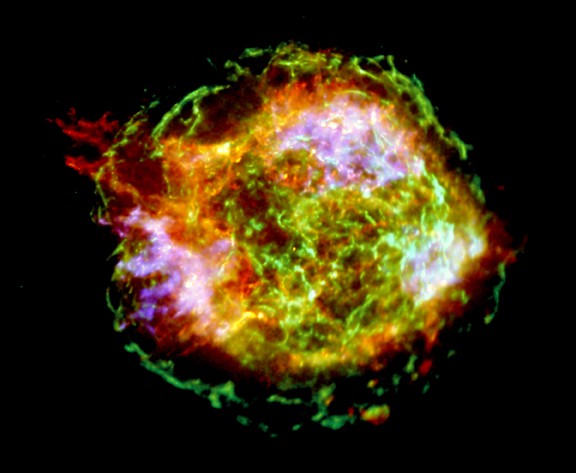
26/08/2004
Close-Up of the Lagoon
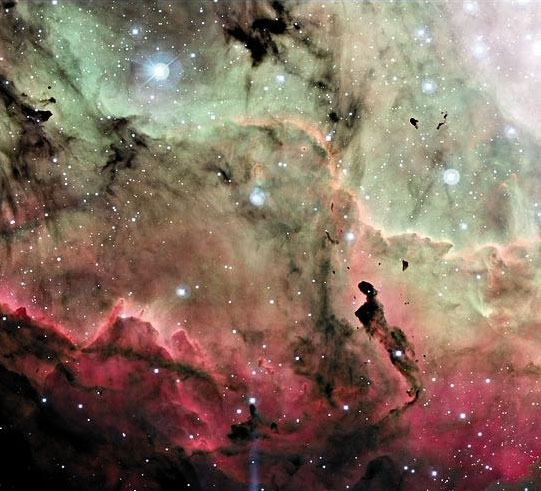

16/08/2004